Ex vivo dissection of optogenetically activated mPFC and hippocampal inputs to neurons in the basolateral amygdala: implications for fear and emotional memory
- PMID: 24634648
- PMCID: PMC3943336
- DOI: 10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00064
Ex vivo dissection of optogenetically activated mPFC and hippocampal inputs to neurons in the basolateral amygdala: implications for fear and emotional memory
Abstract
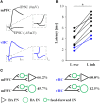
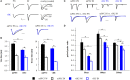
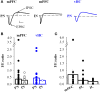
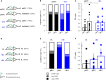
Many lines of evidence suggest that a reciprocally interconnected network comprising the amygdala, ventral hippocampus (vHC), and medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) participates in different aspects of the acquisition and extinction of conditioned fear responses and fear behavior. This could at least in part be mediated by direct connections from mPFC or vHC to amygdala to control amygdala activity and output. However, currently the interactions between mPFC and vHC afferents and their specific targets in the amygdala are still poorly understood. Here, we use an ex-vivo optogenetic approach to dissect synaptic properties of inputs from mPFC and vHC to defined neuronal populations in the basal amygdala (BA), the area that we identify as a major target of these projections. We find that BA principal neurons (PNs) and local BA interneurons (INs) receive monosynaptic excitatory inputs from mPFC and vHC. In addition, both these inputs also recruit GABAergic feedforward inhibition in a substantial fraction of PNs, in some neurons this also comprises a slow GABAB-component. Amongst the innervated PNs we identify neurons that project back to subregions of the mPFC, indicating a loop between neurons in mPFC and BA, and a pathway from vHC to mPFC via BA. Interestingly, mPFC inputs also recruit feedforward inhibition in a fraction of INs, suggesting that these inputs can activate dis-inhibitory circuits in the BA. A general feature of both mPFC and vHC inputs to local INs is that excitatory inputs display faster rise and decay kinetics than in PNs, which would enable temporally precise signaling. However, mPFC and vHC inputs to both PNs and INs differ in their presynaptic release properties, in that vHC inputs are more depressing. In summary, our data describe novel wiring, and features of synaptic connections from mPFC and vHC to amygdala that could help to interpret functions of these interconnected brain areas at the network level.
Keywords: amygdala; conditioned fear; hippocampus; medial prefrontal cortex; optogenetics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synaptic Targeting of Double-Projecting Ventral CA1 Hippocampal Neurons to the Medial Prefrontal Cortex and Basal Amygdala.J Neurosci. 2017 May 10;37(19):4868-4882. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3579-16.2017. Epub 2017 Apr 6. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28385873 Free PMC article.
-
Ex Vivo Optogenetic Dissection of Fear Circuits in Brain Slices.J Vis Exp. 2016 Apr 5;(110):e53628. doi: 10.3791/53628. J Vis Exp. 2016. PMID: 27077317 Free PMC article.
-
Manipulating fear associations via optogenetic modulation of amygdala inputs to prefrontal cortex.Nat Neurosci. 2017 Jun;20(6):836-844. doi: 10.1038/nn.4523. Epub 2017 Mar 13. Nat Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28288126
-
The Role of Basolateral Amygdala and Medial Prefrontal Cortex in Fear: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2025 Jan 29;17(1):e78198. doi: 10.7759/cureus.78198. eCollection 2025 Jan. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40026920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The intercalated paracapsular islands as a module for integration of signals regulating anxiety in the amygdala.Brain Res. 2012 Oct 2;1476:211-34. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.03.047. Epub 2012 Mar 27. Brain Res. 2012. PMID: 22516107 Review.
Cited by
-
Amygdala-prefrontal interactions in (mal)adaptive learning.Trends Neurosci. 2015 Mar;38(3):158-66. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2014.12.007. Epub 2015 Jan 9. Trends Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25583269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hippocampal network oscillations at the interplay between innate anxiety and learned fear.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019 Jan;236(1):321-338. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-5109-z. Epub 2018 Nov 11. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019. PMID: 30417233 Review.
-
Aberrant cortical projections to amygdala GABAergic neurons contribute to developmental circuit dysfunction following early life stress.iScience. 2022 Dec 5;26(1):105724. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.105724. eCollection 2023 Jan 20. iScience. 2022. PMID: 36582824 Free PMC article.
-
Early postnatal exposure to bicuculline modulates E/I balance and induces ASD-like behavioral phenotypes in mice.Anim Cells Syst (Seoul). 2025 Apr 28;29(1):264-281. doi: 10.1080/19768354.2025.2493258. eCollection 2025. Anim Cells Syst (Seoul). 2025. PMID: 40454245 Free PMC article.
-
Optogenetic dissection of medial prefrontal cortex circuitry.Front Syst Neurosci. 2014 Dec 9;8:230. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2014.00230. eCollection 2014. Front Syst Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25538574 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

