When should a liver resection be performed in patients with liver metastases from neuroendocrine tumours? A systematic review with practice recommendations
- PMID: 24636662
- PMCID: PMC4266436
- DOI: 10.1111/hpb.12225
When should a liver resection be performed in patients with liver metastases from neuroendocrine tumours? A systematic review with practice recommendations
Abstract
Aim: To determine the benefits and risks of hepatic resection versus non-resectional liver-directed treatments in patients with potentially resectable neuroendocrine liver metastases.
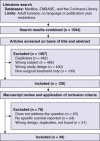
Methods: A systematic review identified 1594 reports which alluded to a possible liver resection for neuroendocrine tumour metastases, of which 38 reports (all retrospective), comprising 3425 patients, were relevant.
Results: Thirty studies reported resection alone, and 16 studies reported overall survival (OS). Only two studies addressed quality-of-life (QoL) issues. Five-year overall survival was reported at 41-100%, whereas 5-year progression-free survival (PFS) was 5-54%. We identified no robust evidence that a liver resection was superior to any other liver-directed therapies in improving OS or PFS. There was no evidence to support the use of a R2 resection (debulking), with or without tumour ablation, to improve either OS or QoL. There was little evidence to guide sequencing of surgery for patients presenting in Stage IV with resectable disease, and none to support a resection of asymptomatic primary tumours in the presence of non-resectable liver metastases.
Conclusion: Low-level recommendations are offered to assist in the management of patients with neuroendocrine liver metastases, along with recommendations for future studies.
© 2014 International Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary Association.
Figures
References
-
- Modlin IM, Oberg K, Chung DC, Jensen RT, de Herder WW, Thakker RV, et al. Gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumours. Lancet Oncol. 2008;9:61–72. - PubMed
-
- Pavel M, Baudin E, Couvelard A, Krenning E, Oberg K, Steinmuller T, et al. ENETS Consensus Guidelines for the management of patients with liver and other distant metastases from neuroendocrine neoplasms of foregut, midgut, hindgut, and unknown primary. Neuroendocrinology. 2012;95:157–176. - PubMed
-
- Gupta S, Johnson MM, Murthy R, Ahrar K, Wallace MJ, Madoff DC, et al. Hepatic arterial embolization and chemoembolization for the treatment of patients with metastatic neuroendocrine tumors: variables affecting response rates and survival. Cancer. 2005;104:1590–1602. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical