Targeted overexpression of tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-4 modifies post-myocardial infarction remodeling in mice
- PMID: 24637197
- PMCID: PMC4040980
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.303634
Targeted overexpression of tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-4 modifies post-myocardial infarction remodeling in mice
Abstract
Rationale: Myocardial infarction (MI) causes an imbalance between matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases (TIMPs) and is associated with adverse left ventricular (LV) remodeling. A uniform reduction in TIMP-4 post-MI has been observed.
Objective: To examine post-MI remodeling with cardiac-restricted overexpression of TIMP-4, either through a transgenic or viral delivery approach.
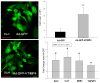
Methods and results: MI was induced in mice and then randomized to targeted injection of an adenoviral construct (10 μL; 8×10(9) plaque forming units/mL) encoding green fluorescent protein (GFP) and the full-length human TIMP-4 (Ad-GFP-TIMP4) or GFP. A transgenic construct with cardiac-restricted overexpression TIMP-4 (hTIMP-4exp) was used in a parallel set of studies. LV end-diastolic volume, an index of LV remodeling, increased by >60% from baseline at 5 days post-MI and by >100% at 21 days post-MI in the Ad-GFP only group. However, LV dilation was reduced by ≈50% in both the Ad-GFP-TIMP4 and hTIMP-4exp groups at these post-MI time points. LV ejection fraction was improved with either Ad-GFP-TIMP-4 or hTIMP-4exp. Fibrillar collagen expression and content were increased within the MI region with both TIMP-4 interventions, suggestive of matrix stabilization.
Conclusions: This study is the first to demonstrate that selective myocardial targeting for TIMP-4 induction through either a viral or transgenic approach favorably altered the course of adverse LV remodeling post-MI. Thus, localized induction of endogenous matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors, such as TIMP-4, holds promise as a means to interrupt the progression of post-MI remodeling.
Keywords: extracellular matrix; myocardial infarction; tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases; ventricular function.
Figures





References
-
- Ikonomidis JS, Hendrick JW, Parkhurst AM, Herron AR, Escobar PG, Dowdy KB, Stroud RE, Hapke E, Zile MR, Spinale FG. Accelerated LV remodeling after myocardial infarction in TIMP-1-deficient mice: effects of exogenous MMP inhibition. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005;288:H149–58. - PubMed
-
- Spinale FG, Escobar GP, Hendrick JW, Clark LL, Camens SS, Mingoia JP, Squires CG, Stroud RE, Ikonomidis JS. Chronic matrix metalloproteinase inhibition following myocardial infarction in mice: differential effects on short and long-term survival. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006;318:966–73. - PubMed
-
- Vanhoutte D, Schellings M, Pinto Y, Heymans S. Relevance of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors after myocardial infarction: a temporal and spatial window. Cardiovasc Res. 2006;69:604–13. - PubMed
-
- Yarbrough WM, Mukherjee R, Escobar GP, Mingoia JT, Sample JA, Hendrick JW, Dowdy KB, McLean JE, Lowry AS, O’Neill TP, Spinale FG. Selective targeting and timing of matrix metalloproteinase inhibition in post-myocardial infarction remodeling. Circulation. 2003;108:1753–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

