Molecular characterization and polyclonal antibody generation against core component CagX protein of Helicobacter pylori type IV secretion system
- PMID: 24637488
- PMCID: PMC4049901
- DOI: 10.4161/bioe.27808
Molecular characterization and polyclonal antibody generation against core component CagX protein of Helicobacter pylori type IV secretion system
Abstract
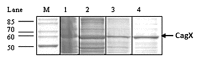
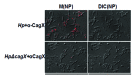
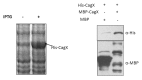
Gram-negative bacteria Helicobacter pylori cause gastric ulcer, duodenal cancer, and found in almost half of the world's residents. The protein responsible for this disease is secreted through type IV secretion system (TFSS) of H. pylori. TFSS is encoded by 40-kb region of chromosomal DNA known as cag-pathogenicity island (PAI). TFSS comprises of three major components: cytoplasmic/inner membrane ATPase, transmembrane core-complex and outer membranous pilli, and associated subunits. Core complex consists of CagX, CagT, CagM, and Cag3(δ) proteins as per existing knowledge. In this study, we have characterized one of the important component of core-complex forming sub-unit protein, i.e., CagX. Complete ORF of CagX except signal peptide coding region was cloned and expressed in pET28a vector. Purification of CagX protein was performed, and polyclonal anti-sera against full-length recombinant CagX were raised in rabbit model. We obtained a very specific and high titer, CagX anti-sera that were utilized to characterize endogenous CagX. Surface localization of CagX was also seen by immunofluorescence microscopy. In short for the first time a full-length CagX was characterized, and we showed that CagX is the part of high molecular weight core complex, which is important for assembly and function of H. pylori TFSS.
Keywords: Cag-PAI; CagX; H. pylori; molecular characterization; type IV secretion system.
Figures




Similar articles
-
C-terminal domain of CagX is responsible for its interaction with CagT protein of Helicobacter pylori type IV secretion system.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Jan 2;456(1):98-103. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.11.041. Epub 2014 Nov 21. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015. PMID: 25446105
-
In Situ Molecular Architecture of the Helicobacter pylori Cag Type IV Secretion System.mBio. 2019 May 14;10(3):e00849-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00849-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31088930 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and Structural Analysis of the Helicobacter pylori cag Type IV Secretion System Core Complex.mBio. 2016 Jan 12;7(1):e02001-15. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02001-15. mBio. 2016. PMID: 26758182 Free PMC article.
-
[The type IV secretion system encoded by the cag PAI of Helicobacter pylori].Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2007 Aug;47(4):743-5. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2007. PMID: 17944386 Review. Chinese.
-
Helicobacter pylori-host cell interactions mediated by type IV secretion.Cell Microbiol. 2005 Jul;7(7):911-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2005.00541.x. Cell Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15953024 Review.
Cited by
-
Helicobacter pylori promotes inflammatory factor secretion and lung injury through VacA exotoxin-mediated activation of NF-κB signaling.Bioengineered. 2022 May;13(5):12760-12771. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2071011. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35603777 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
