Condensed tannins from Ficus virens as tyrosinase inhibitors: structure, inhibitory activity and molecular mechanism
- PMID: 24637701
- PMCID: PMC3956756
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091809
Condensed tannins from Ficus virens as tyrosinase inhibitors: structure, inhibitory activity and molecular mechanism
Abstract
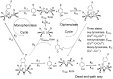
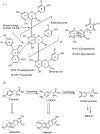
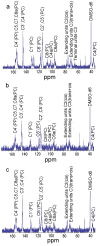
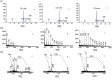
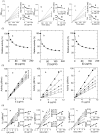
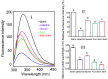
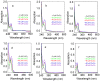
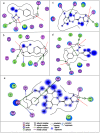
Condensed tannins from Ficus virens leaves, fruit, and stem bark were isolated and their structures characterized by 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometry, high performance liquid chromatography electrospray ionization mass spectrometry, and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. The results showed that the leaves, fruit, and stem bark condensed tannins were complex mixtures of homo- and heteropolymers of B-type procyanidins and prodelphinidins with degrees of polymerization up to hexamer, dodecamer, and pentadecamer, respectively. Antityrosinase activities of the condensed tannins were studied. The results indicated that the condensed tannins were potent tyrosinase inhibitors. The concentrations for the leaves, fruit, and stem bark condensed tannins leading to 50% enzyme activity were determined to be 131.67, 99.89, and 106.22 μg/ml on monophenolase activity, and 128.42, 43.07, and 74.27 μg/ml on diphenolase activity. The inhibition mechanism, type, and constants of the condensed tannins on the diphenolase activity were further investigated. The results indicated that the condensed tannins were reversible and mixed type inhibitors. Fluorescence quenching, copper interacting, and molecular docking techniques were utilized to unravel the molecular mechanisms of the inhibition. The results showed that the hydroxyl group on the B ring of the condensed tannins could chelate the dicopper irons of the enzyme. Moreover, the condensed tannins could reduce the enzyme product o-quinones into colourless compounds. These results would contribute to the development and design of antityrosinase agents.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
NMR, HPLC-ESI-MS, and MALDI-TOF MS analysis of condensed tannins from Delonix regia (Bojer ex Hook.) Raf. and their bioactivities.J Agric Food Chem. 2012 May 16;60(19):5013-22. doi: 10.1021/jf300740d. Epub 2012 May 3. J Agric Food Chem. 2012. PMID: 22515734
-
Avocado Proanthocyanidins as a Source of Tyrosinase Inhibitors: Structure Characterization, Inhibitory Activity, and Mechanism.J Agric Food Chem. 2015 Aug 26;63(33):7381-7. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b03099. Epub 2015 Aug 13. J Agric Food Chem. 2015. PMID: 26259028
-
Isolation and purification of condensed tannins from flamboyant tree and their antioxidant and antityrosinase activities.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2014 May;173(1):179-92. doi: 10.1007/s12010-014-0828-z. Epub 2014 Mar 27. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 24671565
-
Considerations about the inhibition of monophenolase and diphenolase activities of tyrosinase. Characterization of the inhibitor concentration which generates 50 % of inhibition, type and inhibition constants. A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 May;267(Pt 2):131513. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131513. Epub 2024 Apr 10. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38608979 Review.
-
Suicide inactivation of the diphenolase and monophenolase activities of tyrosinase.IUBMB Life. 2010 Jul;62(7):539-47. doi: 10.1002/iub.348. IUBMB Life. 2010. PMID: 20552645 Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis of Triazole Schiff's Base Derivatives and Their Inhibitory Kinetics on Tyrosinase Activity.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 30;10(9):e0138578. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138578. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26422245 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Melanogenic Effect from Submerged Mycelial Cultures of Ganoderma weberianum.Mycobiology. 2019 Feb 23;47(1):112-119. doi: 10.1080/12298093.2019.1568680. eCollection 2019 Mar. Mycobiology. 2019. PMID: 30988994 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical Constituents from Streblus taxoides Wood with Their Antibacterial and Antityrosinase Activities Plus in Silico Study.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Feb 3;12(2):319. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12020319. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36830230 Free PMC article.
-
Procyanidins Negatively Affect the Activity of the Phosphatases of Regenerating Liver.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 30;10(7):e0134336. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134336. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26226290 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Inhibiting Effect of Phytochemicals in Rheum palmatum on Tyrosinase Based on Metabolomics and Isobologram Analyses.Molecules. 2023 Jan 17;28(3):944. doi: 10.3390/molecules28030944. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36770612 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhuang JX, Hu YH, Yang MH, Liu FJ, Qiu L, et al. (2010) Irreversible competitive inhibitory kinetics of cardol triene on mushroom tyrosinase. J Agric Food Chem 58: 12993–12998. - PubMed
-
- Lee N, Kim EJ, Kim BG (2012) Regioselective hydroxylation of trans-resveratrol via inhibition of tyrosinase from Streptomyces avermitilis MA4680. Chem Biol 7: 1687–1692. - PubMed
-
- Lin J Y, Fisher D E (2007) Melanocyte biology and skin pigmentation. Nature 445: 843–850. - PubMed
-
- Choi H, Ahn S, Lee BG, Chang I, Hwang JS (2005) Inhibition of skin pigmentation by an extract of Lepidium apetalum and its possible implication in IL-6 mediated signaling. Pigment Cell Res 18: 439–446. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

