Transcriptional profiles of cytokine/chemokine factors of immune cell-homing to the parasitic lesions: a comprehensive one-year course study in the liver of E. multilocularis-infected mice
- PMID: 24637903
- PMCID: PMC3956718
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091638
Transcriptional profiles of cytokine/chemokine factors of immune cell-homing to the parasitic lesions: a comprehensive one-year course study in the liver of E. multilocularis-infected mice
Abstract
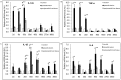
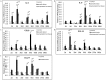
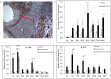
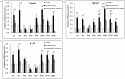
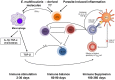
Pathogenesis of chronically developing alveolar echinococcosis (AE) is characterized by a continuous, granulomatous, periparasitic infiltration of immune cells surrounding the metacestode of Echinococcus multilocularis (E.multilocularis) in the affected liver. A detailed cytokine and chemokine profile analysis of the periparasitic infiltrate in the liver has, however, not yet been carried out in a comprehensive way all along the whole course of infection in E. multilocularis intermediate hosts. We thus assessed the hepatic gene expression profiles of 18 selected cytokine and chemokine genes using qRT-PCR in the periparasitic immune reaction and the subsequent adjacent, not directly affected, liver tissue of mice from day 2 to day 360 post intra-hepatic injection of metacestode. DNA microarray analysis was also used to get a more complete picture of the transcriptional changes occurring in the liver surrounding the parasitic lesions. Profiles of mRNA expression levels in the hepatic parasitic lesions showed that a mixed Th1/Th2 immune response, characterized by the concomitant presence of IL-12α, IFN-γ and IL-4, was established very early in the development of E. multilocularis. Subsequently, the profile extended to a combined tolerogenic profile associating IL-5, IL-10 and TGF-β. IL-17 was permanently expressed in the liver, mostly in the periparasitic infiltrate; this was confirmed by the increased mRNA expression of both IL-17A and IL-17F from a very early stage, with a subsequent decrease of IL-17A after this first initial rise. All measured chemokines were significantly expressed at a given stage of infection; their expression paralleled that of the corresponding Th1, Th2 or Th17 cytokines. In addition to giving a comprehensive insight in the time course of cytokines and chemokines in E. multilocularis lesion, this study contributes to identify new targets for possible immune therapy to minimize E. multilocularis-related pathology and to complement the only parasitostatic effect of benzimidazoles in AE.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Vuitton DA (2003) The ambiguous role of immunity in echinococcosis: protection of the host or of the parasite? Acta Trop 85: 119–132. - PubMed
-
- Vuitton DA, Zhang SL, Yang Y, Godot V, Beurton I, et al. (2006) Survival strategy of Echinococcus multilocularis in the human host. Parasitol Int 55 Suppl: S51–55. - PubMed
-
- Manfras BJ, Reuter S, Wendland T, Boehm BO, Kern P (2004) Impeded Th1 CD4 memory T cell generation in chronic-persisting liver infection with Echinococcus multilocularis. Int Immunol 16: 43–50. - PubMed
-
- Emery I, Liance M, Deriaud E, Vuitton DA, Houin R, et al. (1996) Characterization of T-cell immune responses of Echinococcus multilocularis-infected C57BL/6J mice. Parasite Immunol 18: 463–472. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

