Sex-related differences in access to care among patients with premature acute coronary syndrome
- PMID: 24638026
- PMCID: PMC3986312
- DOI: 10.1503/cmaj.131450
Sex-related differences in access to care among patients with premature acute coronary syndrome
Abstract
Background: Access to care may be implicated in disparities between men and women in death after acute coronary syndrome, especially among younger adults. We aimed to assess sex-related differences in access to care among patients with premature acute coronary syndrome and to identify clinical and gender-related determinants of access to care.
Methods: We studied 1123 patients (18-55 yr) admitted to hospital for acute coronary syndrome and enrolled in the GENESIS-PRAXY cohort study. Outcome measures were door-to-electrocardiography, door-to-needle and door-to-balloon times, as well as proportions of patients undergoing cardiac catheterization, reperfusion or nonprimary percutaneous coronary intervention. We performed univariable and multivariable logistic regression analyses to identify clinical and gender-related determinants of timely procedures and use of invasive procedures.
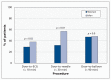
Results: Women were less likely than men to receive care within benchmark times for electrocardiography (≤ 10 min: 29% v. 38%, p = 0.02) or fibrinolysis (≤ 30 min: 32% v. 57%, p = 0.01). Women with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (MI) were less likely than men to undergo reperfusion therapy (primary percutaneous coronary intervention or fibrinolysis) (83% v. 91%, p = 0.01), and women with non-ST-segment elevation MI or unstable angina were less likely to undergo nonprimary percutaneous coronary intervention (48% v. 66%, p < 0.001). Clinical determinants of poorer access to care included anxiety, increased number of risk factors and absence of chest pain. Gender-related determinants included feminine traits of personality and responsibility for housework.
Interpretation: Among younger adults with acute coronary syndrome, women and men had different access to care. Moreover, fewer than half of men and women with ST-segment elevation MI received timely primary coronary intervention. Our results also highlight that men and women with no chest pain and those with anxiety, several traditional risk factors and feminine personality traits were at particularly increased risk of poorer access to care.
Figures
Comment in
-
[Urgent cardiac care. Men received faster care].Perspect Infirm. 2014 Nov-Dec;11(5):54. Perspect Infirm. 2014. PMID: 25438438 French. No abstract available.
References
-
- Lansky AJ, Pietras C, Costa RA, et al. Gender differences in outcomes after primary angioplasty versus primary stenting with and without abciximab for acute myocardial infarction: results of the Controlled Abciximab and Device Investigation to Lower Late Angioplasty Complications (CADILLAC) Trial. Circulation 2005;111:1611–8 - PubMed
-
- Valente S, Lazzeri C, Chiostri M, et al. Gender-related difference in ST-elevation myocardial infarction treated with primary angioplasty: a single-centre 6-year registry. Eur J Prev Cardiol 2012; 19:233–40 - PubMed
-
- Jneid H, Fonarow GC, Cannon CP, et al. Sex differences in medical care and early death after acute myocardial infarction. Circulation 2008;118:2803–10 - PubMed
-
- Tamis-Holland JE, Palazzo A, Stebbins AL, et al. Benefits of direct angioplasty for women and men with acute myocardial infarction: results of the Global Use of Strategies to Open Occluded Arteries in Acute Coronary Syndromes Angioplasty (GUSTO II-B) Angioplasty Substudy. Am Heart J 2004;147:133–9 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources