Cerebrospinal fluid biomarker and brain biopsy findings in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus
- PMID: 24638077
- PMCID: PMC3956805
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091974
Cerebrospinal fluid biomarker and brain biopsy findings in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus
Abstract
Background: The significance of amyloid precursor protein (APP) and neuroinflammation in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (iNPH) and Alzheimer's disease (AD) is unknown.
Objective: To investigate the role of soluble APP (sAPP) and amyloid beta (Aβ) isoforms, proinflammatory cytokines, and biomarkers of neuronal damage in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in relation to brain biopsy Aβ and hyperphosphorylated tau (HPτ) findings.
Methods: The study population comprised 102 patients with possible NPH with cortical brain biopsies, ventricular and lumbar CSF samples, and DNA available. The final clinical diagnoses were: 53 iNPH (91% shunt-responders), 26 AD (10 mixed iNPH+AD), and 23 others. Biopsy samples were immunostained against Aβ and HPτ. CSF levels of AD-related biomarkers (Aβ42, p-tau, total tau), non-AD-related Aβ isoforms (Aβ38, Aβ40), sAPP isoforms (sAPPα, sAPPβ), proinflammatory cytokines (several interleukins (IL), interferon-gamma, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, tumor necrosis factor-alpha) and biomarkers of neuronal damage (neurofilament light and myelin basic protein) were measured. All patients were genotyped for APOE.
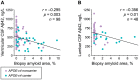
Results: Lumbar CSF levels of sAPPα were lower (p<0.05) in patients with shunt-responsive iNPH compared to non-iNPH patients. sAPPβ showed a similar trend (p = 0.06). CSF sAPP isoform levels showed no association to Aβ or HPτ in the brain biopsy. Quantified Aβ load in the brain biopsy showed a negative correlation with CSF levels of Aβ42 in ventricular (r = -0.295, p = 0.003) and lumbar (r = -0.356, p = 0.01) samples, while the levels of Aβ38 and Aβ40 showed no correlation. CSF levels of proinflammatory cytokines and biomarkers of neuronal damage did not associate to the brain biopsy findings, diagnosis, or shunt response. Higher lumbar/ventricular CSF IL-8 ratios (p<0.001) were seen in lumbar samples collected after ventriculostomy compared to the samples collected before the procedure.
Conclusions: The role of sAPP isoforms in iNPH seems to be independent from the amyloid cascade. No neuroinflammatory background was observed in iNPH or AD.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Time Trends of Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers of Neurodegeneration in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus.J Alzheimers Dis. 2021;80(4):1629-1642. doi: 10.3233/JAD-201361. J Alzheimers Dis. 2021. PMID: 33720890 Free PMC article.
-
CSF biomarkers distinguish idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus from its mimics.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2019 Oct;90(10):1117-1123. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2019-320826. Epub 2019 Jun 5. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 31167811 Free PMC article.
-
Amyloid mis-metabolism in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2016 Jul 29;13(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s12987-016-0037-y. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2016. PMID: 27472944 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus versus Alzheimer's Disease and Subcortical Ischemic Vascular Disease: A Systematic Review.J Alzheimers Dis. 2019;68(1):267-279. doi: 10.3233/JAD-180816. J Alzheimers Dis. 2019. PMID: 30741681
-
Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers as Predictors of Shunt Response in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus: A Systematic Review.Can J Neurol Sci. 2018 Jan;45(1):3-10. doi: 10.1017/cjn.2017.251. Epub 2017 Nov 10. Can J Neurol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29125088
Cited by
-
Hydrocephalus: Molecular and Neuroimaging Biomarkers in Diagnosis and Management.Biomedicines. 2025 Jun 20;13(7):1511. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13071511. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40722587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type Q in cerebrospinal fluid reflects ependymal cell dysfunction and is a potential biomarker for adult chronic hydrocephalus.Eur J Neurol. 2021 Feb;28(2):389-400. doi: 10.1111/ene.14575. Epub 2020 Nov 1. Eur J Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33035386 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial and temporal variation of routine parameters: pitfalls in the cerebrospinal fluid analysis in central nervous system infections.J Neuroinflammation. 2022 Jul 6;19(1):174. doi: 10.1186/s12974-022-02538-3. J Neuroinflammation. 2022. PMID: 35794632 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lumboperitoneal Shunts for the Treatment of Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus: A Comparison of Small-Lumen Abdominal Catheters to Gravitational Add-On Valves in a Single Center.Oper Neurosurg. 2018 Dec 1;15(6):634-642. doi: 10.1093/ons/opy044. Oper Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 29688482 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of cortical tissue analysis in normal pressure hydrocephalus.Cereb Cortex. 2024 Jan 31;34(2):bhae001. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhae001. Cereb Cortex. 2024. PMID: 38275188 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hakim S, Adams RD (1965) The special clinical problem of symptomatic hydrocephalus with normal cerebrospinal fluid pressure. Observations on cerebrospinal fluid hydrodynamics. J Neurol Sci 2: 307–327. - PubMed
-
- Adams RD, Fischer CM, Hakim S, Ojemann RG, Sweet WH (1965) Symptomatic occult hydrocephalus with “normal” cerebrospinal-fluid pressure. A treatable syndrome. N Engl J Med 273: 117–126. - PubMed
-
- Leinonen V, Koivisto AM, Savolainen S, Rummukainen J, Sutela A, et al. (2012) Post-mortem findings in 10 patients with presumed normal-pressure hydrocephalus and review of the literature. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 38: 72–86. - PubMed
-
- Cusimano MD, Rewilak D, Stuss DT, Barrera-Martinez JC, Salehi F, et al. (2011) Normal-pressure hydrocephalus: Is there a genetic predisposition? Can J Neurol Sci 38: 274–281. - PubMed
-
- McGirr A, Cusimano MD (2012) Familial aggregation of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: Novel familial case and a family study of the NPH triad in an iNPH patient cohort. J Neurol Sci 321: 82–88. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

