Cohort profile: project viva
- PMID: 24639442
- PMCID: PMC4339753
- DOI: 10.1093/ije/dyu008
Cohort profile: project viva
Abstract
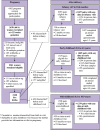
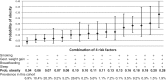
We established Project Viva to examine prenatal diet and other factors in relation to maternal and child health. We recruited pregnant women at their initial prenatal visit in eastern Massachusetts between 1999 and 2002. Exclusion criteria included multiple gestation, inability to answer questions in English, gestational age ≥22 weeks at recruitment and plans to move away before delivery. We completed in-person visits with mothers during pregnancy in the late first (median 9.9 weeks of gestation) and second (median 27.9 weeks) trimesters. We saw mothers and children in the hospital during the delivery admission and during infancy (median age 6.3 months), early childhood (median 3.2 years) and mid-childhood (median 7.7 years). We collected information from mothers via interviews and questionnaires, performed anthropometric and neurodevelopmental assessments and collected biosamples. We have collected additional information from medical records and from mailed questionnaires sent annually to mothers between in-person visits and to children beginning at age 9 years. From 2341 eligible women, there were 2128 live births; 1279 mother-child pairs provided data at the mid-childhood visit. Primary study outcomes include pregnancy outcomes, maternal mental and cardiometabolic health and child neurodevelopment, asthma/atopy and obesity/cardiometabolic health. Investigators interested in learning more about how to obtain Project Viva data can contact Project_Viva@hphc.org.
Keywords: Pregnancy; childhood; cohort; nutrition; obesity.
© The Author 2014; all rights reserved. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the International Epidemiological Association.
Figures
References
-
- White IR, Royston P, Wood AM. Multiple imputation using chained equations: Issues and guidance for practice. Stat Med 2011;30:377–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P30 ES000002/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD 064925/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- K12DK094721/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HD069408/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL 64925/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21DK 073739/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES 016314/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH 068596/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD 034568/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 HD 063590/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL111108/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD 034568-0951/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK 081505/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R03 DE14004/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES21447/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK 082661/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37HD 034568/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK083817/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI102960/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HD 044807/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HD034568/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MD 003963/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL 075504/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA155626/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI 102960/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HL 068041/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD034568/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NR013945/NR/NINR NIH HHS/United States
- K23 ES022242/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

