Identification of transcriptional regulatory elements for Ntng1 and Ntng2 genes in mice
- PMID: 24642214
- PMCID: PMC4000137
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-6606-7-19
Identification of transcriptional regulatory elements for Ntng1 and Ntng2 genes in mice
Abstract
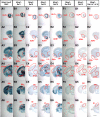
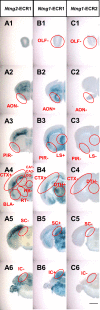
Background: Higher brain function is supported by the precise temporal and spatial regulation of thousands of genes. The mechanisms that underlie transcriptional regulation in the brain, however, remain unclear. The Ntng1 and Ntng2 genes, encoding axonal membrane adhesion proteins netrin-G1 and netrin-G2, respectively, are paralogs that have evolved in vertebrates and are expressed in distinct neuronal subsets in a complementary manner. The characteristic expression patterns of these genes provide a part of the foundation of the cortical layer structure in mammals.
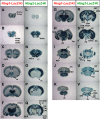
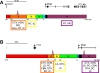
Results: We used gene-targeting techniques, bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC)-aided transgenesis techniques, and in vivo enhancer assays to examine transcriptional mechanisms in vivo to gain insight into how the characteristic expression patterns of these genes are acquired. Analysis of the gene expression patterns in the presence or absence of netrin-G1 and netrin-G2 functional proteins allowed us to exclude the possibility that a feedback or feedforward mechanism mediates their characteristic expression patterns. Findings from the BAC deletion series revealed that widely distributed combinations of cis-regulatory elements determine the differential gene expression patterns of these genes and that major cis-regulatory elements are located in the 85-45 kb upstream region of Ntng2 and in the 75-60 kb upstream region and intronic region of Ntng1. In vivo enhancer assays using 2-kb evolutionarily conserved regions detected enhancer activity in the distal upstream regions of both genes.
Conclusions: The complementary expression patterns of Ntng1 and Ntng2 are determined by transcriptional cis-regulatory elements widely scattered in these loci. The cis-regulatory elements characterized in this study will facilitate the development of novel genetic tools for functionally dissecting neural circuits to better understand vertebrate brain function.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Decreased mRNA expression of netrin-G1 and netrin-G2 in the temporal lobe in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2008 Mar;33(4):933-45. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1301457. Epub 2007 May 16. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2008. PMID: 17507910 Free PMC article.
-
Diversification of behavior and postsynaptic properties by netrin-G presynaptic adhesion family proteins.Mol Brain. 2016 Jan 8;9:6. doi: 10.1186/s13041-016-0187-5. Mol Brain. 2016. PMID: 26746425 Free PMC article.
-
A family-based association study and gene expression analyses of netrin-G1 and -G2 genes in schizophrenia.Biol Psychiatry. 2005 Feb 15;57(4):382-93. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2004.11.022. Biol Psychiatry. 2005. PMID: 15705354
-
Cis-regulatory landscapes in development and evolution.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2017 Apr;43:17-22. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2016.10.004. Epub 2016 Nov 11. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2017. PMID: 27842294 Review.
-
Deep conservation of cis-regulatory elements in metazoans.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013 Nov 11;368(1632):20130020. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0020. Print 2013 Dec 19. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24218633 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetically Engineered Brain Organoids Recapitulate Spatial and Developmental States of Glioblastoma Progression.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Mar;12(10):e2410110. doi: 10.1002/advs.202410110. Epub 2025 Jan 21. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 39836549 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic and neurochemical analysis of the stellate ganglia in mice highlights sex differences.Sci Rep. 2018 Jun 12;8(1):8963. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-27306-3. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29895973 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium imaging reveals glial involvement in transcranial direct current stimulation-induced plasticity in mouse brain.Nat Commun. 2016 Mar 22;7:11100. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11100. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27000523 Free PMC article.
-
Transient Astrocytic Gq Signaling Underlies Remote Memory Enhancement.Front Neural Circuits. 2021 Mar 22;15:658343. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2021.658343. eCollection 2021. Front Neural Circuits. 2021. PMID: 33828463 Free PMC article.
-
Netrin-G/NGL complexes encode functional synaptic diversification.J Neurosci. 2014 Nov 19;34(47):15779-92. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1141-14.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25411505 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

