Motivational salience signal in the basal forebrain is coupled with faster and more precise decision speed
- PMID: 24642480
- PMCID: PMC3958335
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001811
Motivational salience signal in the basal forebrain is coupled with faster and more precise decision speed
Abstract
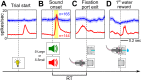
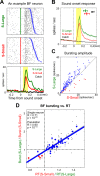
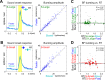
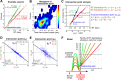
The survival of animals depends critically on prioritizing responses to motivationally salient stimuli. While it is generally believed that motivational salience increases decision speed, the quantitative relationship between motivational salience and decision speed, measured by reaction time (RT), remains unclear. Here we show that the neural correlate of motivational salience in the basal forebrain (BF), defined independently of RT, is coupled with faster and also more precise decision speed. In rats performing a reward-biased simple RT task, motivational salience was encoded by BF bursting response that occurred before RT. We found that faster RTs were tightly coupled with stronger BF motivational salience signals. Furthermore, the fraction of RT variability reflecting the contribution of intrinsic noise in the decision-making process was actively suppressed in faster RT distributions with stronger BF motivational salience signals. Artificially augmenting the BF motivational salience signal via electrical stimulation led to faster and more precise RTs and supports a causal relationship. Together, these results not only describe for the first time, to our knowledge, the quantitative relationship between motivational salience and faster decision speed, they also reveal the quantitative coupling relationship between motivational salience and more precise RT. Our results further establish the existence of an early and previously unrecognized step in the decision-making process that determines both the RT speed and variability of the entire decision-making process and suggest that this novel decision step is dictated largely by the BF motivational salience signal. Finally, our study raises the hypothesis that the dysregulation of decision speed in conditions such as depression, schizophrenia, and cognitive aging may result from the functional impairment of the motivational salience signal encoded by the poorly understood noncholinergic BF neurons.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Comment in
-
How motivation triggers speedy decisions.PLoS Biol. 2014 Mar 18;12(3):e1001812. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001812. eCollection 2014 Mar. PLoS Biol. 2014. PMID: 24642485 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Donders FC (1868) On the speed of mental process. Translated by W G Koster, 1969 Acta Psychol 30: 412–431. - PubMed
-
- Luce D (1986) Response times. New York: Oxford University Press.
-
- Jensen AR (2006) Clocking the mind: mental chronometry and individual differences. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
-
- Nebes RD, Butters MA, Mulsant BH, Pollock BG, Zmuda MD, et al. (2000) Decreased working memory and processing speed mediate cognitive impairment in geriatric depression. Psychol Med 30: 679–691. - PubMed
-
- Den Hartog HM, Derix MMA, Van Bemmel AL, Kremer B, Jolles J (2003) Cognitive functioning in young and middle-aged unmedicated out-patients with major depression: testing the effort and cognitive speed hypotheses. Psychol Med 33: 1443–1451. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

