Postmortem mRNA expression patterns in left ventricular myocardial tissues and their implications for forensic diagnosis of sudden cardiac death
- PMID: 24642708
- PMCID: PMC3969045
- DOI: 10.14348/molcells.2014.2344
Postmortem mRNA expression patterns in left ventricular myocardial tissues and their implications for forensic diagnosis of sudden cardiac death
Abstract
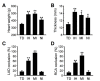
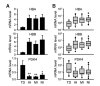
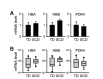
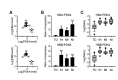
Sudden cardiac death (SCD), which is primarily caused by lethal heart disorders resulting in structural and arrhythmogenic abnormalities, is one of the prevalent modes of death in most developed countries. Myocardial ischemia, mainly due to coronary artery disease, is the most common type of heart disease leading to SCD. However, postmortem diagnosis of SCD is frequently complicated by obscure histological evidence. Here, we show that certain mRNA species, namely those encoding hemoglobin A1/2 and B (Hba1/2 and Hbb, respectively) as well as pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 (Pdk4), exhibit distinct postmortem expression patterns in the left ventricular free wall of SCD subjects when compared with their expression patterns in the corresponding tissues from control subjects with non-cardiac causes of death. Hba1/2 and Hbb mRNA expression levels were higher in ischemic SCD cases with acute myocardial infarction or ischemic heart disease without recent infarction, and even in cardiac death subjects without apparent pathological signs of heart injuries, than control subjects. By contrast, Pdk4 mRNA was expressed at lower levels in SCD subjects. In conclusion, we found that altered myocardial Hba1/2, Hbb, and Pdk4 mRNA expression patterns can be employed as molecular signatures of fatal cardiac dysfunction to forensically implicate SCD as the primary cause of death.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential expression of B-type natriuretic peptide between left and right ventricles, with particular regard to sudden cardiac death.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Oct;16(4):4763-4769. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7136. Epub 2017 Aug 2. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28765973 Free PMC article.
-
[Expression of Brain Natriuretic Peptide in Myocardial Tissue of Sudden Cardiac Death and Non-sudden Cardiac Death].Fa Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2017 Dec;33(6):587-591. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5619.2017.06.003. Epub 2017 Dec 25. Fa Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 29441763 Chinese.
-
mRNA expression patterns in human myocardial tissue, pericardial fluid and blood, and its contribution to the diagnosis of cause of death.Forensic Sci Int. 2019 Sep;302:109876. doi: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2019.109876. Epub 2019 Jul 25. Forensic Sci Int. 2019. PMID: 31419595
-
Sudden cardiac death in the young: the molecular autopsy and a practical approach to surviving relatives.Eur Heart J. 2015 Jun 1;36(21):1290-6. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv063. Epub 2015 Mar 11. Eur Heart J. 2015. PMID: 25765769 Review.
-
The use of cardiac troponin T (cTnT) in the postmortem diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction and sudden cardiac death: A systematic review.Forensic Sci Int. 2018 Nov;292:27-38. doi: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2018.09.002. Epub 2018 Sep 17. Forensic Sci Int. 2018. PMID: 30269044
Cited by
-
Low-Level Light Therapy Downregulates Scalp Inflammatory Biomarkers in Men With Androgenetic Alopecia and Boosts Minoxidil 2% to Bring a Sustainable Hair Regrowth Activity.Lasers Surg Med. 2021 Nov;53(9):1208-1219. doi: 10.1002/lsm.23398. Epub 2021 May 11. Lasers Surg Med. 2021. PMID: 33973663 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of Iron Metabolism-Linked Genes at Myocardial Tissue and Cell Levels in Dilated Cardiomyopathy.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 2;24(3):2887. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032887. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36769209 Free PMC article.
-
Cell Death-Associated Ribosomal RNA Cleavage in Postmortem Tissues and Its Forensic Applications.Mol Cells. 2017 Jun 30;40(6):410-417. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2017.0039. Epub 2017 Jun 15. Mol Cells. 2017. PMID: 28614917 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA Expression in CD4+ T Cells in Neurosyphilis Patients.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Nov 8;7:461. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00461. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29167762 Free PMC article.
-
Early Protective Role of Inflammation in Cardiac Remodeling and Heart Failure: Focus on TNFα and Resident Macrophages.Cells. 2022 Apr 6;11(7):1249. doi: 10.3390/cells11071249. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35406812 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alvarez-Guardia D., Palomer X., Coll T., Davidson M.M., Chan T.O., Feldman A.M., Laguna J.C., Vázquez-Carrera M. The p65 subunit of NF-kappaB binds to PGC-1alpha, linking inflammation and metabolic disturbances in cardiac cells. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010;87:449–458. - PubMed
-
- Arab S., Konstantinov I.E., Boscarino C., Cukerman E., Mori A., Li J., Liu P.P., Redington A.N., Coles J.G. Early gene expression profiles during intraoperative myocardial ischemia-reperfusion in cardiac surgery. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2007;134:74–81. - PubMed
-
- Carturan E., Tester D.J., Brost B.C., Basso C., Thiene G., Ackerman M.J. Postmortem genetic testing for conventional autopsy-negative sudden unexplained death: an evaluation of different DNA extraction protocols and the feasibility of mutational analysis from archival paraffin-embedded heart tissue. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2006;129:391–397. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

