Fast-dissolving core-shell composite microparticles of quercetin fabricated using a coaxial electrospray process
- PMID: 24643072
- PMCID: PMC3958439
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092106
Fast-dissolving core-shell composite microparticles of quercetin fabricated using a coaxial electrospray process
Abstract
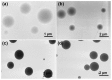
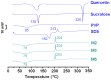
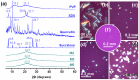
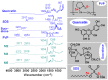
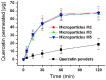
This study reports on novel fast-dissolving core-shell composite microparticles of quercetin fabricated using coaxial electrospraying. A PVC-coated concentric spinneret was developed to conduct the electrospray process. A series of analyses were undertaken to characterize the resultant particles in terms of their morphology, the physical form of their components, and their functional performance. Scanning and transmission electron microscopies revealed that the microparticles had spherical morphologies with clear core-shell structure visible. Differential scanning calorimetry and X-ray diffraction verified that the quercetin active ingredient in the core and sucralose and sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) excipients in the shell existed in the amorphous state. This is believed to be a result of second-order interactions between the components; these could be observed by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. In vitro dissolution and permeation studies showed that the microparticles rapidly released the incorporated quercetin within one minute, and had permeation rates across the sublingual mucosa around 10 times faster than raw quercetin.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Liang X, Li J, Joo JB, Gutierrez A, Tillekarathe A, et al. (2012) Diffusion through the shells of yolk–shell and core–shell nanostructures in the liquid phase. Angew Chem Int Ed 51: 8034–8036. - PubMed
-
- Wu J, Kong T, Yeung KWK, Shum HC, Cheung KMC, et al. (2013) Fabrication and characterization of monodisperse PLGA–alginate core–shell microspheres with monodisperse size and homogeneous shells for controlled drug release. Acta Biomater 9: 7410–7419. - PubMed
-
- Chaudhuri RG, Paria S (2012) Core/shell nanoparticles: classes, properties, synthesis mechanisms, characterization, and applications. Chem Rev 112: 2373–433. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

