Proteomic analysis of detergent resistant membrane domains during early interaction of macrophages with rough and smooth Brucella melitensis
- PMID: 24643124
- PMCID: PMC3958395
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091706
Proteomic analysis of detergent resistant membrane domains during early interaction of macrophages with rough and smooth Brucella melitensis
Abstract
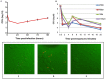
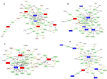
The plasma membrane contains discrete nanometer-sized domains that are resistant to non-ionic detergents, and which are called detergent resistant membrane domains (DRMDs) or lipid rafts. Exposure of host cells to pathogenic bacteria has been shown to induce the re-distribution of specific host proteins between DRMDs and detergent soluble membranes, which leads to the initiation of cell signaling that enable pathogens to access host cells. DRMDs have been shown to play a role in the invasion of Brucella into host macrophages and the formation of replicative phagosomes called Brucella-containing vacuoles (BCVs). In this study we sought to characterize changes to the protein expression profiles in DRMDs and to respective cellular pathways and networks of Mono Mac 6 cells in response to the adherence of rough VTRM1 and smooth 16 M B. melitensis strains. DRMDs were extracted from Mono Mac 6 cells exposed for 2 minutes at 4°C to Brucella (no infection occurs) and from unexposed control cells. Protein expression was determined using the non-gel based quantitative iTRAQ (Isobaric Tags for Relative and Absolute Quantitation) mass spectrometry technique. Using the identified iTRAQ proteins we performed enrichment analyses and probed constructed human biochemical networks for interactions and metabolic reactions. We identified 149 proteins, which either became enriched, depleted or whose amounts did not change in DRMDs upon Brucella exposure. Several of these proteins were distinctly enriched or depleted in DRMDs upon exposure to rough and smooth B. melitensis strains which results in the differential engagement of cellular pathways and networks immediately upon Brucella encounter. For some of the proteins such as myosin 9, small G protein signaling modulator 3, lysine-specific demethylase 5D, erlin-2, and voltage-dependent anion-selective channel protein 2, we observed extreme differential depletion or enrichment in DRMDs. The identified proteins and pathways could provide the basis for novel ways of treating or diagnosing Brucellosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Colmenero JD, Reguera JM, Martos F, Sanchez-De-Mora D, Delgado M, et al. (1996) Complications associated with Brucella melitensis infection: a study of 530 cases. Medicine 75: 195–211. - PubMed
-
- Solera J (2010) Update on brucellosis: therapeutic challenges. International journal of antimicrobial agents 36 Suppl 1S18–20. - PubMed
-
- Corbel MJ (2006) Brucellosis in humans and animals.
-
- Foster G, Osterman BS, Godfroid J, Jacques I, Cloeckaert A (2007) Brucella ceti sp. nov. and Brucella pinnipedialis sp. nov. for Brucella strains with cetaceans and seals as their preferred hosts. International journal of systematic and evolutionary microbiology 57: 2688–2693. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

