Noninvasive assessment of hepatic fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B viral infection using magnetic resonance elastography
- PMID: 24643284
- PMCID: PMC3955787
- DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2014.15.2.210
Noninvasive assessment of hepatic fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B viral infection using magnetic resonance elastography
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the diagnostic performance of magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) for staging hepatic fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection.
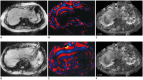
Materials and methods: Patients with chronic HBV infection who were suspected of having focal or diffuse liver diseases (n = 195) and living donor candidates (n = 166) underwent MRE as part of the routine liver MRI examination. We measured liver stiffness (LS) values on quantitative shear stiffness maps. The technical success rate of MRE was then determined. Liver cell necroinflammatory activity and fibrosis were assessed using histopathologic examinations as the reference. Areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve (Az) were calculated in order to predict the liver fibrosis stage.
Results: The technical success rate of MRE was 92.5% (334/361). The causes of technical failure were poor wave propagation (n = 12), severe respiratory motion (n = 3), or the presence of iron deposits in the liver (n = 12). The mean LS values, as measured by MRE, increased significantly along with an increase in the fibrosis stage (r = 0.901, p < 0.001); however, the mean LS values did not increase significantly along with the degree of necroinflammatory activity. The cutoff values of LS for ≥ F1, ≥ F2, ≥ F3, and F4 were 2.45 kPa, 2.69 kPa, 3.0 kPa, and 3.94 kPa, respectively, and with Az values of 0.987-0.988.
Conclusion: MRE has a high technical success rate and excellent diagnostic accuracy for staging hepatic fibrosis in patients with chronic HBV infection.
Keywords: Hepatic fibrosis; Hepatitis B; Liver; Liver cirrhosis; MRE; Magnetic resonance imaging.
Figures
References
-
- Han KH, Yoon KT. New diagnostic method for liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. Intervirology. 2008;51(Suppl 1):11–16. - PubMed
-
- Bensamoun SF, Wang L, Robert L, Charleux F, Latrive JP, Ho Ba Tho MC. Measurement of liver stiffness with two imaging techniques: magnetic resonance elastography and ultrasound elastometry. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2008;28:1287–1292. - PubMed
-
- McGill DB, Rakela J, Zinsmeister AR, Ott BJ. A 21-year experience with major hemorrhage after percutaneous liver biopsy. Gastroenterology. 1990;99:1396–1400. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

