Gene regulatory networks governing lung specification
- PMID: 24644080
- PMCID: PMC4263286
- DOI: 10.1002/jcb.24810
Gene regulatory networks governing lung specification
Abstract
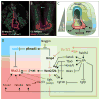
The epithelial lining of the respiratory system originates from a small group of progenitor cells in the ventral foregut endoderm of the early embryo. Research in the last decade has revealed a number of paracrine signaling pathways that are critical for the development of these respiratory progenitors. In the post-genomic era the challenge now is to figure out at the genome wide level how these different signaling pathways and their downstream transcription factors interact in a complex "gene regulatory network" (GRN) to orchestrate early lung development. In this prospective, we review our growing understanding of the GRN governing lung specification. We discuss key gaps in our knowledge and describe emerging opportunities that will soon provide an unprecedented understanding of lung development and accelerate our ability to apply this knowledge to regenerative medicine.
Keywords: GENE REGULATORY NETWORK; LUNG DEVELOPMENT; Nkx2.1; RESPIRATORY EPITHELIUM; SPECIFICATION.
© 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Molecular atlas of Xenopus respiratory system development.Dev Dyn. 2015 Jan;244(1):69-85. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.24180. Epub 2014 Sep 11. Dev Dyn. 2015. PMID: 25156440 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial cells are not required for specification of respiratory progenitors.Dev Biol. 2017 Jul 1;427(1):93-105. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2017.05.003. Epub 2017 May 10. Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 28501476 Free PMC article.
-
Pluripotent stem cell differentiation reveals distinct developmental pathways regulating lung- versus thyroid-lineage specification.Development. 2017 Nov 1;144(21):3879-3893. doi: 10.1242/dev.150193. Epub 2017 Sep 25. Development. 2017. PMID: 28947536 Free PMC article.
-
Formation of the Embryonic Head in the Mouse: Attributes of a Gene Regulatory Network.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2016;117:497-521. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2015.11.019. Epub 2016 Feb 15. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 26969997 Review.
-
The embryonic origins and genetic programming of emerging haematopoietic stem cells.FEBS Lett. 2016 Nov;590(22):4002-4015. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12363. Epub 2016 Sep 1. FEBS Lett. 2016. PMID: 27531714 Review.
Cited by
-
Meta-Analysis of Gene Expression and Identification of Biological Regulatory Mechanisms in Alzheimer's Disease.Front Neurosci. 2019 Jul 3;13:633. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00633. eCollection 2019. Front Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31333395 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling of Respiratory Diseases Evolving with Fibrosis from Organoids Derived from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 23;24(5):4413. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054413. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36901843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Maverick Review of Common Stem/Progenitor Markers in Lung Development.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022 Dec;18(8):2629-2645. doi: 10.1007/s12015-022-10422-z. Epub 2022 Jul 23. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022. PMID: 35871209 Review.
-
Evolutionarily conserved Tbx5-Wnt2/2b pathway orchestrates cardiopulmonary development.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Nov 6;115(45):E10615-E10624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1811624115. Epub 2018 Oct 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30352852 Free PMC article.
-
Application of iPSC to Modelling of Respiratory Diseases.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1237:1-16. doi: 10.1007/5584_2019_430. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 31468358 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aubin J, Lemieux M, Tremblay M, Berard J, Jeannotte L. Early postnatal lethality in Hoxa-5 mutant mice is attributable to respiratory tract defects. Dev Biol. 1997;192:432–445. - PubMed
-
- Bolouri H. Computational modeling of gene regulatory networks: a primer. Imperial College Press; London: 2008.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

