Efficacy and safety of duloxetine in the treatment of older adult patients with generalized anxiety disorder: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
- PMID: 24644106
- PMCID: PMC4285965
- DOI: 10.1002/gps.4088
Efficacy and safety of duloxetine in the treatment of older adult patients with generalized anxiety disorder: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
Abstract
Objective: This was a flexible-dosed study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of duloxetine 30-120 mg once daily in the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) in older adult patients.
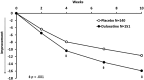
Methods: Patients with GAD, who were at least 65 years of age, were randomly assigned to double-blind treatment with either duloxetine (N = 151) or placebo (N = 140). The primary efficacy measure was the Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HAM-A) total score, and the primary endpoint was at week 10. Global functioning was assessed by the Sheehan Disability Scale (SDS). Safety and tolerability was assessed by the occurrence of treatment-emergent adverse events, serious adverse events, laboratory analyses, and vital signs. Analyses were conducted on an intent-to-treat basis.
Results: The overall baseline mean HAM-A total score was 24, and SDS global score was 14. Completion rates were 75% for placebo and 76% for duloxetine. At week 10, duloxetine was superior to placebo on mean changes from baseline in HAM-A total scores (-15.9 vs. -11.7, p < 0.001) and in SDS global scores (-8.6 vs. -5.4, p < 0.001). Treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in ≥5% of duloxetine-treated patients and twice the rate than with placebo including constipation (9% vs. 4%, p = 0.06), dry mouth (7% vs. 1%, p = 0.02), and somnolence (6% vs. 2%, p = 0.14).
Conclusion: Duloxetine treatment was efficacious in the improvement of anxiety and functioning in older adult patients with GAD, and the safety profile was consistent with previous GAD studies.
Keywords: anxiety; duloxetine; functioning.
© 2014 The Authors. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Allgulander C, Nutt D, Detke M. A non-inferiority comparison of duloxetine and venlafaxine in the treatment of adult patients with generalized anxiety disorder. J Psychopharmacol. 2008;22(4):417–425. - PubMed
-
- Allgulander C, Hackett D, Salinas E. Venlafaxine extended release (ER) in the treatment of generalised anxiety disorder: twenty-four-week placebo-controlled dose-ranging study. Br J Psychiatry. 2001;179:15–22. - PubMed
-
- Allgulander C, Florea I, Huusom AK. Prevention of relapse in generalized anxiety disorder by escitalopram treatment. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2006;9(5):495–505. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4th edn. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 1994.
-
- Baldwin DS, Allgulander C, Bandelow B, Ferre F, Pallanti S. An international survey of reported prescribing practice in the treatment of patients with generalised anxiety disorder. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2012;13(7):510–516. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

