Engagement of the small GTPase Rab31 protein and its effector, early endosome antigen 1, is important for trafficking of the ligand-bound epidermal growth factor receptor from the early to the late endosome
- PMID: 24644286
- PMCID: PMC4007434
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.548321
Engagement of the small GTPase Rab31 protein and its effector, early endosome antigen 1, is important for trafficking of the ligand-bound epidermal growth factor receptor from the early to the late endosome
Abstract
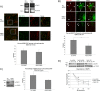
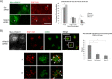
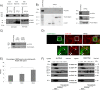
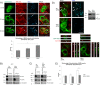
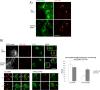
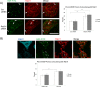
Rab31 is a member of the Rab5 subfamily of Rab GTPases. Although localized largely to the trans-Golgi network, it shares common guanine nucleotide exchange factors and effectors with other Rab5 subfamily members that have been implicated in endocytic membrane traffic. We investigated whether Rab31 also has a role in the trafficking of the ligand-bound EGF receptor (EGFR) internalized through receptor-mediated endocytosis. We found that loss of Rab31 inhibits, but overexpression enhances, EGFR trafficking to the late endosomes and that the effect of Rab31 silencing could be specifically rescued by overexpression of a silencing-resistant form of Rab31. Rab31 was found to interact with the EGFR by coimmunoprecipitation and affinity pulldown analyses, and the primarily trans-Golgi network-localized Rab31 has increased colocalization with the EGFR in A431 cells 30 min after pulsing with EGF. A glycerol gradient sedimentation assay suggested that Rab31 is sequestered into a high molecular weight complex after stimulation with EGF, as was early endosome antigen 1 (EEA1), a factor responsible for endosomal tethering and fusion events. We found that loss of EEA1 reduced the interaction between Rab31 and the EGFR and abrogated the effect of Rab31 overexpression on the trafficking of the EGFR. Likewise, loss of GAPex5, a Rab31 guanine nucleotide exchange factor that has a role in ubiquitination and degradation of the EGFR, reduced the interaction of Rab31 with the EGFR and its effect on EGFR trafficking. Taken together, our results suggest that Rab31 is an important regulator of endocytic trafficking of the EGFR and functions in an EGFR trafficking complex that includes EEA1 and GAPex5.
Keywords: Endocytosis; Endosomes; Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR); Rab; Trafficking.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Characterization of RIN3 as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for the Rab5 subfamily GTPase Rab31.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jul 8;286(27):24364-73. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.172445. Epub 2011 May 17. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21586568 Free PMC article.
-
rab7 activity affects epidermal growth factor:epidermal growth factor receptor degradation by regulating endocytic trafficking from the late endosome.J Biol Chem. 2006 Jan 13;281(2):1099-106. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M504175200. Epub 2005 Nov 10. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16282324
-
A role for the small GTPase Rab21 in the early endocytic pathway.J Cell Sci. 2004 Dec 15;117(Pt 26):6297-311. doi: 10.1242/jcs.01560. Epub 2004 Nov 23. J Cell Sci. 2004. PMID: 15561770
-
The role of the small GTPase Rab31 in cancer.J Cell Mol Med. 2015 Jan;19(1):1-10. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12403. Epub 2014 Dec 3. J Cell Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25472813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Who's in control? Principles of Rab GTPase activation in endolysosomal membrane trafficking and beyond.J Cell Biol. 2021 Sep 6;220(9):e202105120. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202105120. Epub 2021 Aug 12. J Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 34383013 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Spontaneous preterm birth: the underpinnings in the maternal and fetal genomes.NPJ Genom Med. 2021 Jun 8;6(1):43. doi: 10.1038/s41525-021-00209-5. NPJ Genom Med. 2021. PMID: 34103530 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of Small GTPases in Acquired Tamoxifen Resistance in MCF-7 Cells Revealed by Targeted, Quantitative Proteomic Analysis.Anal Chem. 2018 Dec 18;90(24):14551-14560. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.8b04526. Epub 2018 Nov 30. Anal Chem. 2018. PMID: 30431262 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of RAB31 silencing on osteosarcoma cell proliferation and migration through the Hedgehog signaling pathway.J Bone Miner Metab. 2019 Jul;37(4):594-606. doi: 10.1007/s00774-018-0961-9. Epub 2018 Nov 23. J Bone Miner Metab. 2019. Retraction in: J Bone Miner Metab. 2022 May;40(3):539. doi: 10.1007/s00774-022-01316-8. PMID: 30470957 Retracted.
-
RIN1 promotes renal cell carcinoma malignancy by activating EGFR signaling through Rab25.Cancer Sci. 2017 Aug;108(8):1620-1627. doi: 10.1111/cas.13297. Epub 2017 Jul 3. Cancer Sci. 2017. PMID: 28612496 Free PMC article.
-
Rab31 and APPL2 enhance FcγR-mediated phagocytosis through PI3K/Akt signaling in macrophages.Mol Biol Cell. 2015 Mar 1;26(5):952-65. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E14-10-1457. Epub 2015 Jan 7. Mol Biol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25568335 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Markgraf D. F., Peplowska K., Ungermann C. (2007) Rab cascades and tethering factors in the endomembrane system. FEBS Lett. 581, 2125–2130 - PubMed
-
- Seabra M. C., Coudrier E. (2004) Rab GTPases and myosin motors in organelle motility. Traffic 5, 393–399 - PubMed
-
- Li L. (2001) Direct interaction of Rab4 with syntaxin 4. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 5265–5273 - PubMed
-
- Simonsen A. (1999) The Rab5 effector EEA1 interacts directly with syntaxin-6. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 28857–28860 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

