Comparison of Two brands of Methylphenidate (Stimdate(®) vs. Ritalin(®)) in Children and Adolescents with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Double-Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 24644466
- PMCID: PMC3939941
Comparison of Two brands of Methylphenidate (Stimdate(®) vs. Ritalin(®)) in Children and Adolescents with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Double-Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Objective: To compare the effectiveness and safety of the methylphenidate produced in Iran (Stimdate®) with its original brand (Ritalin®) in children with Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
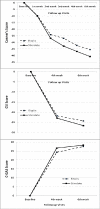
Methods: In this double-blinded randomized clinical trial, 30 patients with ADHD who were 6 to 16 years old, were divided into two groups: 15 in Stimdate® and 15 in Ritalin® group. The two groups were compared for side effects profile, Conner's Parent's Rating Scale-Persion version (CPRS-R), Child Symptom Inventory-4 (CSI-4), Clinical Global Impressions (CGI), and Children's Global Assessment Scale (CGAS), at baseline and at the 4(th) and 6(th) weeks.
Results: The subjects showed significant decreases in the CPRS-Rand CSI-4 scores and significant increase of CGAS scores during the follow-up, but there were no significant difference between Stimdate® and Ritalin® group, regarding the pattern of changes observed. The mean therapeutic dose and the number of side effects were not significantly different between the two studied groups.
Conclusions: Both Stimdate® and Ritalin® had comparable clinical efficacy and safety in children with ADHD.
Keywords: ADHD; Ritalin; Side effects; Stimdate; Therapeutic effect.
Figures
References
-
- Biederman J. Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a life-span perspective. J Clin Psychiatry. 1998;59(7):4–16. - PubMed
-
- Faraone SV, Biederman J, Spencer T, Wilens T, Seidman LJ, Mick E, et al. Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in adults: an overview. Biol Psychiatry. 2000;48(1):9–20. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-IV-TR) 4th ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 1994.
-
- Barkley RA, Fischer M, Smallish L, Fletcher K. Young adult outcome of hyperactive children. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2006;45(2):192–202. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources