Tea polyphenols induced apoptosis of breast cancer cells by suppressing the expression of Survivin
- PMID: 24646833
- PMCID: PMC3960584
- DOI: 10.1038/srep04416
Tea polyphenols induced apoptosis of breast cancer cells by suppressing the expression of Survivin
Abstract
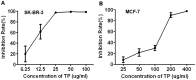
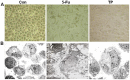
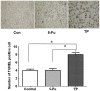
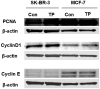
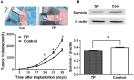
To study the mechanism of tea polyphenols (TP)-induced apoptosis of breast cancer cells. Proliferation of MCF-7 and SK-BR-3 cells was evaluated by MTT assays. Cellular ultrastructure was examined by electron microscopy. Apoptosis was detected by TUNEL. PCNA、 Cyclin D1、 Cyclin E and Survivin expression was measured by Western blot. Cell proliferation was significantly inhibited by TP. Spindle and round cells were loosely distributed with increased particles after TP treatment. Increased cell size, frequent nuclear atypia and a collapse of apoptosis were observed. The nucleus was pushed towards one side, while the cytoplasm was rich in free ribosome. The membrane of mitochondria was thickening, and the cell apoptotic body was observed. TP treated cells experienced significantly enhanced apoptosis compared with 5-Fu treated or control groups. The expression of survivin was downregulated by TP. To conclude, TP can inhibit cell growth and induce apoptosis through downregulating the expression of survivin in breast cancer.
Figures

References
-
- Butt M. S. & Sultan M. T. Green tea: nature's defense against malignancies. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 49, 463–473 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Xi J., Xue Y., Xu Y. & Shen Y. Artificial neural network modeling and optimization of ultrahigh pressure extraction of green tea polyphenols. Food Chem. 141, 320–326 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Qin Y., Guo X. W., Li L., Wang H. W. & Kim W. The antioxidant property of chitosan green tea polyphenols complex induces transglutaminase activation in wound healing. J Med Food. 16, 487–498 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

