Involvement of the BDNF gene in loneliness in adolescence: a report of opposite gene effects in boys and girls
- PMID: 24647525
- PMCID: PMC3960275
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092768
Involvement of the BDNF gene in loneliness in adolescence: a report of opposite gene effects in boys and girls
Abstract
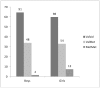
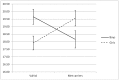
Previous research has shown that loneliness has a heritable component and that genes within the serotonin-, dopamine-, and oxytocin systems are related to loneliness in adolescence. In the present study, the relation between the BDNF Val66Met polymorphism and loneliness in adolescent boys and girls was examined in a longitudinal study spanning five annual waves (N = 305). Latent growth curve modeling (LGCM) was used to examine the baseline level and the change in loneliness over time. The main finding was that the BDNF gene was not related to loneliness in the total sample. A BDNF by sex interaction was found, in that Met carrying girls had the highest levels of loneliness at baseline, whereas in boys the ValVal genotype was related to higher levels of loneliness. Our results underline the importance of sex-stratified analyses when examining effects of the BDNF genotype and the necessity of conducting gene studies to intermediate phenotypes of loneliness.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oxytocin receptor gene (OXTR) in relation to loneliness in adolescence: interactions with sex, parental support, and DRD2 and 5-HTTLPR genotypes.Psychiatr Genet. 2013 Oct;23(5):204-13. doi: 10.1097/YPG.0b013e328363f631. Psychiatr Genet. 2013. PMID: 23838880
-
BDNF Val66Met polymorphism modulates the effect of loneliness on white matter microstructure in young adults.Biol Psychol. 2017 Dec;130:41-49. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2017.10.002. Epub 2017 Oct 5. Biol Psychol. 2017. PMID: 28988974
-
The dopamine D2 receptor gene, perceived parental support, and adolescent loneliness: longitudinal evidence for gene-environment interactions.J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2011 Oct;52(10):1044-51. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.2011.02424.x. Epub 2011 Jun 15. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 21675993 Clinical Trial.
-
Genotypes do not confer risk for delinquency but rather alter susceptibility to positive and negative environmental factors: gene-environmentinteractions of BDNF Val66Met, 5-HTTLPR, and MAOA-uVNTR [corrected].Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014 Dec 10;18(5):pyu107. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyu107. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25522433 Free PMC article.
-
The Val66Met brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene variant interacts with early pain exposure to predict cortisol dysregulation in 7-year-old children born very preterm: Implications for cognition.Neuroscience. 2017 Feb 7;342:188-199. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.08.044. Epub 2015 Aug 28. Neuroscience. 2017. PMID: 26318333 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Loneliness: An Immunometabolic Syndrome.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Nov 19;18(22):12162. doi: 10.3390/ijerph182212162. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34831917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-Wide Association Study of Loneliness Demonstrates a Role for Common Variation.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2017 Mar;42(4):811-821. doi: 10.1038/npp.2016.197. Epub 2016 Sep 15. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2017. PMID: 27629369 Free PMC article.
-
Neurogenetics and Epigenetics of Loneliness.Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2023 Nov 29;16:4839-4857. doi: 10.2147/PRBM.S423802. eCollection 2023. Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2023. PMID: 38050640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adolescent Loneliness and the Interaction between the Serotonin Transporter Gene (5-HTTLPR) and Parental Support: A Replication Study.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 17;10(7):e0133430. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133430. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26186217 Free PMC article.
-
Perceived Parental Support and Psychological Control, DNA Methylation, and Loneliness: Longitudinal Associations Across Early Adolescence.J Youth Adolesc. 2023 Oct;52(10):1995-2011. doi: 10.1007/s10964-023-01822-6. Epub 2023 Jul 20. J Youth Adolesc. 2023. PMID: 37470939
References
-
- Baumeister RF, Leary MR (1995) The need to belong: desire for interpersonal attachments as a fundamental human motivation. Psychol Bull 117: 497–529. - PubMed
-
- Perlman D, Peplau LA (1981) Toward a social psychology of loneliness. In: Gillmour R, Duck S, editors. Personal Relationships 3: Personal Relationships in Disorder. London: Academic Press. 31–56.
-
- Gardner WL, Pickett CL, Jefferis V, Knowles M (2005) On the outside looking in: loneliness and social monitoring. Pers Soc Psychol Bull 31: 1549–1560. - PubMed
-
- Rotenberg KJ, Addis N, Betts LR, Corrigan A, Fox C, et al. (2010) The relation between trust beliefs and loneliness during early childhood, middle childhood, and adulthood. Pers Soc Psychol Bull 36: 1086–1100. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous