Ischemic factor-induced increases in cerebral microvascular endothelial cell Na/H exchange activity and abundance: evidence for involvement of ERK1/2 MAP kinase
- PMID: 24647544
- PMCID: PMC4024711
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00021.2013
Ischemic factor-induced increases in cerebral microvascular endothelial cell Na/H exchange activity and abundance: evidence for involvement of ERK1/2 MAP kinase
Abstract
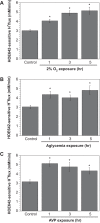
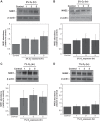
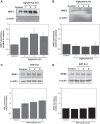
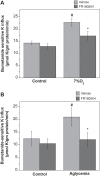
Brain edema forms rapidly in the early hours of ischemic stroke by increased secretion of Na, Cl, and water into the brain across an intact blood-brain barrier (BBB), together with swelling of astrocytes as they take up the ions and water crossing the BBB. Our previous studies provide evidence that luminal BBB Na-K-Cl cotransport (NKCC) and Na/H exchange (NHE) participate in ischemia-induced edema formation. NKCC1 and two NHE isoforms, NHE1 and NHE2, reside predominantly at the luminal BBB membrane. NKCC and NHE activities of cerebral microvascular endothelial cells (CMEC) are rapidly stimulated by the ischemic factors hypoxia, aglycemia, and AVP, and inhibition of NKCC and NHE activities by bumetanide and HOE642, respectively, reduces brain Na uptake and edema in the rat middle cerebral artery occlusion model of stroke. The present study was conducted to further explore BBB NHE responses to ischemia. We examined whether ischemic factor-stimulated NHE activity is sustained over several hours, when the majority of edema forms during stroke. We also examined whether ischemic factors alter NHE1 and/or NHE2 protein abundance. Finally, we conducted initial studies of ERK1/2 MAP kinase involvement in BBB NHE and NKCC responses to ischemic factors. We found that hypoxia, aglycemia, and AVP increase CMEC NHE activity through 5 h and that NHE1, but not NHE2, abundance is increased by 1- to 5-h exposures to these factors. Furthermore, we found that these factors rapidly increase BBB ERK1/2 activity and that ERK1/2 inhibition reduces or abolishes ischemic factor stimulation of NKCC and NHE activities.
Keywords: ERK1/2 MAP kinase; FR180204; HOE642; blood-brain barrier; cerebral edema; stroke.
Copyright © 2014 the American Physiological Society.
Figures


References
-
- Betz AL. Alterations in cerebral endothelial cell function in ischemia. Adv Neurol 71: 301–313, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Bourke RS, Kimelberg HK, Nelson LR, Barron KD, Auen EL, Popp AJ, Waldman JB. Biology of glial swelling in experimental brain edema. Adv Neurol 28: 99–109, 1980 - PubMed
-
- Boyarsky G, Ganz MB, Sterzel RB, Boron WF. pH regulation in single glomerula mesangial cells. I. Acid extrusion in the absence and presence of HCO3−. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 255: C844–C856, 1988 - PubMed
-
- Boyarsky G, Ransom B, Schlue WR, Davis MB, Boron WF. Intracellular pH regulation in single cultured astrocytes from rat forebrain. Glia 8: 241–248, 1993 - PubMed
-
- Brillault J, Lam TI, Rutkowsky JM, Foroutan S, O'Donnell ME. Hypoxia effects on cell volume and ion uptake of cerebral microvascular endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 294: C88–C96, 2008 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

