Metabolic syndrome across Europe: different clusters of risk factors
- PMID: 24647805
- PMCID: PMC4544872
- DOI: 10.1177/2047487314525529
Metabolic syndrome across Europe: different clusters of risk factors
Abstract
Background: Metabolic syndrome (MetS) remains a controversial entity. Specific clusters of MetS components - rather than MetS per se - are associated with accelerated arterial ageing and with cardiovascular (CV) events. To investigate whether the distribution of clusters of MetS components differed cross-culturally, we studied 34,821 subjects from 12 cohorts from 10 European countries and one cohort from the USA in the MARE (Metabolic syndrome and Arteries REsearch) Consortium.
Methods: In accordance with the ATP III criteria, MetS was defined as an alteration three or more of the following five components: elevated glucose (G), fasting glucose ≥110 mg/dl; low HDL cholesterol, < 40mg/dl for men or <50 mg/dl for women; high triglycerides (T), ≥150 mg/dl; elevated blood pressure (B), ≥130/≥85 mmHg; abdominal obesity (W), waist circumference >102 cm for men or >88 cm for women.
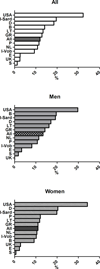
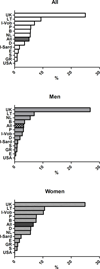
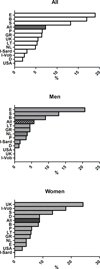
Results: MetS had a 24.3% prevalence (8468 subjects: 23.9% in men vs. 24.6% in women, p < 0.001) with an age-associated increase in its prevalence in all the cohorts. The age-adjusted prevalence of the clusters of MetS components previously associated with greater arterial and CV burden differed across countries (p < 0.0001) and in men and women (p < 0.0001). In details, the cluster TBW was observed in 12% of the subjects with MetS, but was far more common in the cohorts from the UK (32.3%), Sardinia in Italy (19.6%), and Germany (18.5%) and less prevalent in the cohorts from Sweden (1.2%), Spain (2.6%), and the USA (2.5%). The cluster GBW accounted for 12.7% of subjects with MetS with higher occurrence in Southern Europe (Italy, Spain, and Portugal: 31.4, 18.4, and 17.1% respectively) and in Belgium (20.4%), than in Northern Europe (Germany, Sweden, and Lithuania: 7.6, 9.4, and 9.6% respectively).
Conclusions: The analysis of the distribution of MetS suggested that what follows under the common definition of MetS is not a unique entity rather a constellation of cluster of MetS components, likely selectively risky for CV disease, whose occurrence differs across countries.
Keywords: Blood pressure; Europe; HDL cholesterol; epidemiology; glucose; metabolic syndrome; triglycerides; waist circumference.
© The European Society of Cardiology 2014 Reprints and permissions: sagepub.co.uk/journalsPermissions.nav.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: None
Figures






References
-
- Reaven GM. The metabolic syndrome: requiescat in pace. Clin Chem. 2005;51:931–938. - PubMed
-
- Grundy SM. The metabolic syndrome still lives. Clin Chem. 2005;51:1352–1354. - PubMed
-
- Scuteri A, Najjar SS, Morrell CH, Lakatta EG. The metabolic syndrome in older individuals: prevalence and prediction of cardiovascular events: the Cardiovascular Health Study. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:882–887. - PubMed
-
- Mottillo S, Filion KB, Genest J, Joseph L, Pilote L, Poirier P, Rinfret S, Schiffrin EL, Eisenberg MJ. The metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular risk a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;56:1113–1132. - PubMed
-
- Kondo T, Osugi S, Shimokata K, Honjo H, Morita Y, Yamashita K, Maeda K, Muramatsu T, Shintani S, Matsushita K, Murohara T. Metabolic syndrome and all-cause mortality, cardiac events, and cardiovascular events: a follow-up study in 25,471 young- and middle-aged Japanese men. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil. 2011;18:574–580. (2011) Epub 2011 Feb 14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

