Exposure to inhomogeneous static magnetic field beneficially affects allergic inflammation in a murine model
- PMID: 24647908
- PMCID: PMC4006248
- DOI: 10.1098/rsif.2014.0097
Exposure to inhomogeneous static magnetic field beneficially affects allergic inflammation in a murine model
Abstract
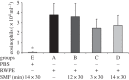
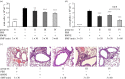
Previous observations suggest that static magnetic field (SMF)-exposure acts on living organisms partly through reactive oxygen species (ROS) reactions. In this study, we aimed to define the impact of SMF-exposure on ragweed pollen extract (RWPE)-induced allergic inflammation closely associated with oxidative stress. Inhomogeneous SMF was generated with an apparatus validated previously providing a peak-to-peak magnetic induction of the dominant SMF component 389 mT by 39 T m(-1) lateral gradient in the in vivo and in vitro experiments, and 192 mT by 19 T m(-1) in the human study at the 3 mm target distance. Effects of SMF-exposure were studied in a murine model of allergic inflammation and also in human provoked skin allergy. We found that even a single 30-min exposure of mice to SMF immediately following intranasal RWPE challenge significantly lowered the increase in the total antioxidant capacity of the airways and decreased allergic inflammation. Repeated (on 3 consecutive days) or prolonged (60 min) exposure to SMF after RWPE challenge decreased the severity of allergic responses more efficiently than a single 30-min treatment. SMF-exposure did not alter ROS production by RWPE under cell-free conditions, while diminished RWPE-induced increase in the ROS levels in A549 epithelial cells. Results of the human skin prick tests indicated that SMF-exposure had no significant direct effect on provoked mast cell degranulation. The observed beneficial effects of SMF are likely owing to the mobilization of cellular ROS-eliminating mechanisms rather than direct modulation of ROS production by pollen NAD(P)H oxidases.
Keywords: allergic inflammation; oxidative stress; pollen; static magnetic field.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Influence of inhomogeneous static magnetic field-exposure on patients with erosive gastritis: a randomized, self- and placebo-controlled, double-blind, single centre, pilot study.J R Soc Interface. 2014 Sep 6;11(98):20140601. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2014.0601. J R Soc Interface. 2014. PMID: 25008086 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Lateral gradients significantly enhance static magnetic field-induced inhibition of pain responses in mice--a double blind experimental study.Bioelectromagnetics. 2013 Jul;34(5):385-96. doi: 10.1002/bem.21781. Epub 2013 Feb 15. Bioelectromagnetics. 2013. PMID: 23737187
-
Exposure to an inhomogeneous static magnetic field increases thermal pain threshold in healthy human volunteers.Bioelectromagnetics. 2011 Feb;32(2):131-9. doi: 10.1002/bem.20622. Epub 2010 Oct 28. Bioelectromagnetics. 2011. PMID: 21225890 Clinical Trial.
-
The effects of static magnetic fields on bone.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2014 May;114(3):146-52. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2014.02.001. Epub 2014 Feb 18. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24556024 Review.
-
[Static magnetic fields and its biomedical effects].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2013 Feb;30(1):176-90. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 23488161 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Homogeneous static magnetic field of different orientation induces biological changes in subacutely exposed mice.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016 Jan;23(2):1584-97. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-5109-z. Epub 2015 Sep 17. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016. PMID: 26377971
-
Combined Photobiomodulation and Static Magnetic Fields to Reduce Side Effects from Laser and Radiofrequency Treatments for Dermatological Conditions.J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2023 Feb;16(2):24-28. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 36909868 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic Fields and Reactive Oxygen Species.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Oct 18;18(10):2175. doi: 10.3390/ijms18102175. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29057846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative transcriptomic analysis revealed important processes underlying the static magnetic field effects on Arabidopsis.Front Plant Sci. 2024 May 28;15:1390031. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1390031. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38863539 Free PMC article.
-
Spinning magnetic field patterns that cause oncolysis by oxidative stress in glioma cells.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 7;13(1):19264. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-46758-w. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37935811 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Calhoun WJ, Reed HE, Moest DR, Stevens CA. 1992. Enhanced superoxide production by alveolar macrophages and air-space cells, airway inflammation, and alveolar macrophage density changes after segmental antigen bronchoprovocation in allergic subjects. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 145, 317–325. (10.1164/ajrccm/145.2_Pt_1.317) - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

