Impaired flexibility in decision making in rats after administration of the pharmacological stressor yohimbine
- PMID: 24647923
- PMCID: PMC4345043
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-014-3529-y
Impaired flexibility in decision making in rats after administration of the pharmacological stressor yohimbine
Abstract
Rationale: Stress-induced disruption of decision making has been hypothesized to contribute to drug-seeking behaviors and addiction. Noradrenergic signaling plays a central role in mediating stress responses. However, the effects of acute stress on decision making, and the role of noradrenergic signaling in regulating these effects, have not been well characterized.
Objective: To characterize changes in decision making caused by acute pharmacological stress, the effects of yohimbine (an α2-adrenergic antagonist) were examined in a delay discounting task. Noradrenergic contributions to decision making were further characterized by examining the effects of propranolol (a β antagonist), prazosin (an α1 antagonist), and guanfacine (an α2 agonist).
Methods: Sprague-Dawley rats were administered drugs prior to performance on a delay discounting task, in which the delay preceding the large reward increased within each session (ascending delays). To dissociate drug-induced changes in delay sensitivity from behavioral inflexibility, drug effects were subsequently tested in a modified version of the discounting task, in which the delay preceding the large reward decreased within each session (descending delays).
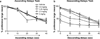
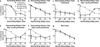
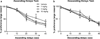
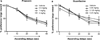
Results: Yohimbine increased choice of the large reward when tested with ascending delays but decreased choice of the same large reward when tested with descending delays, suggesting that drug effects could be attributed to perseverative choice of the lever preferred at the beginning of the session. Propranolol increased choice of the large reward when tested with ascending delays. Prazosin and guanfacine had no effect on reward choice.
Conclusions: The stress-like effects of yohimbine administration may impair decision making by causing inflexible, perseverative behavior.
Figures

References
-
- Alexander JK, Hillier A, Smith RM, Tivarus ME, Beversdorf DQ. Beta-adrenergic modulation of cognitive flexibility during stress. J Cogn Neurosci. 2007;19:468–478. - PubMed
-
- Arnsten AF, Mathew R, Ubriani R, Taylor JR, Li BM. Alpha-1 noradrenergic receptor stimulation impairs prefrontal cortical cognitive function. Biol Psychiatry. 1999;45:26–31. - PubMed
-
- Aston-Jones G, Rajkowski J, Cohen J. Role of locus coeruleus in attention and behavioral flexibility. Biol Psychiatry. 1999;46:1309–1320. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

