Comparison of creatinine and specific gravity for hydration corrections on measurement of the tobacco-specific nitrosamine 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanol (NNAL) in urine
- PMID: 24648246
- PMCID: PMC6807571
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.21693
Comparison of creatinine and specific gravity for hydration corrections on measurement of the tobacco-specific nitrosamine 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanol (NNAL) in urine
Abstract
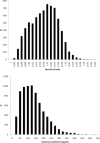
Background: Tobacco-specific carcinogen 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanol (NNAL) was measured in all participants aged 6 years and older from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007-2008. The suitability of using creatinine or specific gravity for urinary NNAL correction in exposure assessment is examined in this study.
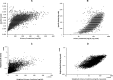
Methods: Effects of both specific gravity and creatinine correction on urinary NNAL among smokers were investigated with multiple linear regression models using either normalization or the fitting of creatinine and specific gravity in the model as covariates.
Results: When log-scaled NNAL was normalized by either creatinine or specific gravity, R(2) was slightly higher for creatinine than for specific gravity (R(2) = 0.1694 and 0.1439, for creatinine and specific gravity, respectively). When log-scaled NNAL was normalized by both factors, the R(2) was improved (R(2) = 0.2068). When specific gravity or creatinine was included as a covariate separately in the models, they were highly significant factors (P < 0.001, R(2) = 0.2226 and 0.1681 for creatinine and specific gravity, respectively). However, when both were included in the model as covariates, creatinine remained highly significant (P < 0.001), whereas the significance of specific gravity was eliminated (P = 0.4294).
Conclusion: This study confirms significant relationships between NNAL concentrations and both urine creatinine and specific gravity. We conclude that creatinine is the more influential and preferred variable to account for urine dilution in tobacco-specific nitrosamine exposure assessment.
Keywords: 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanol (NNAL); creatinine; specific gravity; tobacco-specific nitrosamine.
© 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tobacco-specific nitrosamine 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanol (NNAL) in smokers in the United States: NHANES 2007-2008.Biomarkers. 2011 Mar;16(2):112-9. doi: 10.3109/1354750X.2010.533288. Epub 2010 Nov 29. Biomarkers. 2011. PMID: 21114376
-
Genetic variability in the metabolism of the tobacco-specific nitrosamine 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK) to 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanol (NNAL).Int J Cancer. 2012 Mar 15;130(6):1338-46. doi: 10.1002/ijc.26162. Epub 2011 Aug 3. Int J Cancer. 2012. PMID: 21544809 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of maternal tobacco smoking or exposure to second-hand smoke on the levels of 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanol (NNAL) in urine of mother and the first urine of newborn.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2011 Jun;62(3):377-83. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21893699
-
Direct analysis of tobacco-specific nitrosamine NNK and its metabolite NNAL in human urine by LC-MS/MS: evidence of linkage to methylated DNA lesions.Arch Toxicol. 2014 Feb;88(2):291-9. doi: 10.1007/s00204-013-1137-y. Epub 2013 Sep 22. Arch Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 24057573
-
Comparison of urine cotinine and the tobacco-specific nitrosamine metabolite 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanol (NNAL) and their ratio to discriminate active from passive smoking.Nicotine Tob Res. 2011 Mar;13(3):202-8. doi: 10.1093/ntr/ntq237. Epub 2011 Jan 21. Nicotine Tob Res. 2011. PMID: 21330276 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Concentrations of Cotinine and 4-(Methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-Pyridyl)-1-Butanol (NNAL) in U.S. Non-Daily Cigarette Smokers.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2021 Jun;30(6):1165-1174. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-20-1601. Epub 2021 Mar 18. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2021. PMID: 33737303 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated Levels of Urinary 8-oxodG Correlate with Persistent Periductal Fibrosis after Praziquantel Treatment in Chronic Opisthorchiasis.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2018 Jun;98(6):1763-1769. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.17-0971. Epub 2018 Apr 5. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2018. PMID: 29637887 Free PMC article.
-
Adjusting urinary chemical biomarkers for hydration status during pregnancy.J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. 2018 Sep;28(5):481-493. doi: 10.1038/s41370-018-0043-z. Epub 2018 Jun 8. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. 2018. PMID: 29880833 Free PMC article.
-
A cross-validation based approach for estimating specific gravity in elementary-school aged children using a nonlinear model.Environ Res. 2023 Jan 15;217:114793. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.114793. Epub 2022 Nov 19. Environ Res. 2023. PMID: 36414110 Free PMC article.
-
Stereospecific Metabolism of the Tobacco-Specific Nitrosamine, NNAL.Chem Res Toxicol. 2015 Nov 16;28(11):2112-9. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.5b00278. Epub 2015 Oct 28. Chem Res Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 26452127 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xia Y, McGuffey JE, Bhattacharyya S, et al. Analysis of the tobacco‐specific nitrosamine 4‐(methyinitrosamino)‐1‐(3‐pyridyl)‐1‐butanol in urine by extraction on a molecularly imprinted polymer column and liquid chromatography/atmospheric pressure ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 2005;77(23):7639–7645. - PubMed
-
- Hecht SS, Carmella SG, Murphy SE, Akerkar S, Brunnemann KD, Hoffmann D. A tobacco‐specific lung carcinogen in the urine of men exposed to cigarette‐smoke. New Engl J Med 1993;329(21):1543–1546. - PubMed
-
- Hecht SS, Trushin N. DNA and hemoglobin alkylation by 4‐(methylnitrosamino)‐1‐(3‐pyridyl)‐1‐butanone and its major metabolite 4‐(methylnitrosamino)‐1‐(3‐pyridyl)‐1‐butanol in F344 rats. Carcinogenesis 1988;9(9):1665–1668. - PubMed
-
- Hecht SS. Biochemistry, biology, and carcinogenicity of tobacco‐specific N‐nitrosamines. Chem Res Toxicol 1998;11(6):559–603. - PubMed
-
- Hoffmann D, Djordjevic MV, Rivenson A, Zang E, Desai D, Amin S. A study of tobacco carcinogenesis. LI. Relative potencies of tobacco‐specific N‐nitrosamines as inducers of lung tumours in A/J mice. Cancer Lett 1993;71(1–3):25–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

