Lung tumourigenesis in a conditional Cul4A transgenic mouse model
- PMID: 24648314
- PMCID: PMC4084828
- DOI: 10.1002/path.4352
Lung tumourigenesis in a conditional Cul4A transgenic mouse model
Abstract
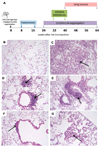
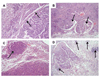
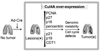
Cullin4A (Cul4A) is a scaffold protein that assembles cullin-RING ubiquitin ligase (E3) complexes and regulates many cellular events, including cell survival, development, growth and cell cycle control. Our previous study suggested that Cul4A is oncogenic in vitro, but its oncogenic role in vivo has not been studied. Here, we used a Cul4A transgenic mouse model to study the potential oncogenic role of Cul4A in lung tumour development. After Cul4A over-expression was induced in the lungs for 32 weeks, atypical epithelial cells were observed. After 40 weeks, lung tumours were visible and were characterized as grade I or II adenocarcinomas. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) revealed decreased levels of Cul4A-associated proteins p21(CIP1) and tumour suppressor p19(ARF) in the lung tumours, suggesting that Cul4A regulated their expression in these tumours. Increased levels of p27(KIP1) and p16(INK4a) were also detected in these tumours. Moreover, the protein level of DNA replication licensing factor CDT1 was decreased. Genomic instability in the lung tumours was further analysed by the results from pericentrin protein expression and array comparative genomic hybridization analysis. Furthermore, knocking down Cul4A expression in lung cancer H2170 cells increased their sensitivity to the chemotherapy drug cisplatin in vitro, suggesting that Cul4A over-expression is associated with cisplatin resistance in the cancer cells. Our findings indicate that Cul4A is oncogenic in vivo, and this Cul4A mouse model is a tool in understanding the mechanisms of Cul4A in human cancers and for testing experimental therapies targeting Cul4A.
Keywords: Ad-Cre; Cul4A; cell cycle; non-small cell lung cancer; transgenic mouse models.
Copyright © 2014 Pathological Society of Great Britain and Ireland. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
CUL4high Lung Adenocarcinomas Are Dependent on the CUL4-p21 Ubiquitin Signaling for Proliferation and Survival.Am J Pathol. 2021 Sep;191(9):1638-1650. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2021.05.018. Epub 2021 Jun 11. Am J Pathol. 2021. PMID: 34119472 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of cullin 4A inhibits growth and increases chemosensitivity in lung cancer cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2016 Jul;20(7):1295-306. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12811. Epub 2016 Mar 10. J Cell Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 26969027 Free PMC article.
-
PR-Set7 is Degraded in a Conditional Cul4A Transgenic Mouse Model of Lung Cancer.Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2015 Jun;18(6):345-50. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2015.06.15. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26104890 Free PMC article.
-
The CUL4A ubiquitin ligase is a potential therapeutic target in skin cancer and other malignancies.Chin J Cancer. 2013 Sep;32(9):478-82. doi: 10.5732/cjc.012.10279. Epub 2013 Jul 12. Chin J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23845142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CUL4A ubiquitin ligase: a promising drug target for cancer and other human diseases.Open Biol. 2014 Feb 12;4(2):130217. doi: 10.1098/rsob.130217. Open Biol. 2014. PMID: 24522884 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SIRT3 promotion reduces resistance to cisplatin in lung cancer by modulating the FOXO3/CDT1 axis.Cancer Med. 2021 Feb;10(4):1394-1404. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3728. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 33655712 Free PMC article.
-
CUL4high Lung Adenocarcinomas Are Dependent on the CUL4-p21 Ubiquitin Signaling for Proliferation and Survival.Am J Pathol. 2021 Sep;191(9):1638-1650. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2021.05.018. Epub 2021 Jun 11. Am J Pathol. 2021. PMID: 34119472 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Cullin-RING E3 Ubiquitin Ligase 4 by Small Molecule Modulators.J Cell Signal. 2021;2(3):195-205. doi: 10.33696/Signaling.2.051. J Cell Signal. 2021. PMID: 34604860 Free PMC article.
-
CUL4A silencing attenuates cervical carcinogenesis and improves Cisplatin sensitivity.Mol Cell Biochem. 2024 May;479(5):1041-1058. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04776-2. Epub 2023 Jun 7. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 37285039
-
Cul4A overexpression associated with Gli1 expression in malignant pleural mesothelioma.J Cell Mol Med. 2015 Oct;19(10):2385-96. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12620. Epub 2015 Jul 27. J Cell Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 26218750 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen LC, Manjeshwar S, Lu Y, et al. The human homologue for the Caenorhabditis elegans cul-4 gene is amplified and overexpressed in primary breast cancers. Cancer Res. 1998;58:3677–3683. - PubMed
-
- Shinomiya T, Mori T, Ariyama Y, et al. Comparative genomic hybridization of squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: the possible involvement of the DPI gene in the 13q34 amplicon. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1999;24:337–344. - PubMed
-
- Yasui K, Arii S, Zhao C, et al. TFDP1, CUL4A, and CDC16 identified as targets for amplification at 13q34 in hepatocellular carcinomas. Hepatology. 2002;35:1476–1484. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

