Population-based service mammography screening: the Icelandic experience
- PMID: 24648754
- PMCID: PMC3929328
- DOI: 10.2147/BCTT.S44671
Population-based service mammography screening: the Icelandic experience
Abstract
Objective: This study analyzes the efficacy of the Icelandic population-based service mammography screening.
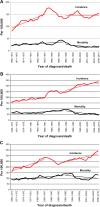
Material and methods: Women aged 40-69 were invited for screening at 2-year intervals starting in November 1987. The study evaluates: (A) attendance and other screened performance parameters during 1998-2010; (B) trends in age-standardized and age-specific incidence rates during 1969-2010 and mortality rates during 1969-2010; and (C) distribution of risk factors and disease specific death rates according to mode of detection.
Results: (A) In the age group of 40-69, the average 2-year attendance was 62%, recall rate was 4.1%, needle biopsy rate was 1.3%, surgery rate was 0.6%, invasive cancer rate was 0.4%, and ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) rate was 0.06%. (B) The linear incidence trend after the start of screening decreased significantly in the age group 40-49, increased significantly in the age group 50-69, but decreased non-significantly in the age group 70-79. The decreased age-specific incidence in the 70-79 age group was, however, greater than the increased age-specific incidence at the ages 50-69. The mortality rate decreased 41% for all age groups and the linear mortality trend decreased significantly at ages 40-49, 50-69, and 70-79. In the age group 40-74 years, the age-specific mortality decreased by 6.9 cases per 2000 during a 10-year period. (C) Screen-detected women had significantly smaller tumors, more favorable tumor grade, fewer axillary metastases and, after correction for other risk factors, the likelihood of dying from cancer decreased 54% (hazard ratio: 0.46; 95% confidence interval: 0.31-0.69) for these patients compared to cases of nonparticipators.
Conclusion: The study results confirm acceptable rates of recalls and referrals for further diagnosis and treatment, and significantly decreased breast cancer mortality rate after starting screening.
Keywords: breast cancer; incidence; mammography; mode of detection; mortality; risk factors; screening.
Figures

References
-
- Nyström L, Rutqvist LE, Wall S, et al. Breast cancer screening with mammography: overview of Swedish randomised trials. Lancet. 1993;341(8851):973–978. - PubMed
-
- The Cochrane Collaboration . Screening for Breast Cancer with Mammography. Copenhagen: The Cochrane Collaboration; 2008. [Accessed April 7, 2013]. Available from: http://www.cochrane.dk/screening/index-en.htm.
-
- Welch HG, Black WC. Overdiagnosis in cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2010;102(9):605–613. - PubMed
-
- US Preventive Services Task Force Screening for breast cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151(10):716–726. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

