Current advances in animal model of chondrosarcoma and related research
- PMID: 24648883
- PMCID: PMC3956875
- DOI: 10.3892/br.2012.13
Current advances in animal model of chondrosarcoma and related research
Abstract
Chondrosarcoma is a type of malignant cartilage tumor with a high local recurrence. Due to its resistance to chemo- and radiotherapy, current treatment is limited to surgical resection. Animal model is one of the most important approaches to studying this disease, although systematic reporting on its development is rare. In this review, we summarized the elements involving animal model establishment. On the basis of these elements, we further classified chondrosarcoma animal models into various types. In addition, we compared various measurements for evaluating the animal model. Finally, its specific applications were discussed.
Keywords: allograft; animal model; chondrosarcoma; heterotopic; orthotopic; xenograft.
Figures
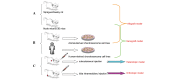
References
-
- Hemmati M, Abbaspour A, Alizadeh AM, et al. Rat xenograft chondrosarcoma development by human tissue fragment. Exp Oncol. 2011;33:52–54. - PubMed
-
- Li TM, Lin TY, Hsu SF, et al. The novel benzimidazole derivative, MPTB, induces cell apoptosis in human chondrosarcoma cells. Mol Carcinog. 2011;50:791–803. - PubMed
-
- Bergh P, Gunterberg B, Meis-Kindblom JM, Kindblom LG. Prognostic factors and outcome of pelvic, sacral, and spinal chondrosarcomas: a center-based study of 69 cases. Cancer. 2001;91:1201–1212. - PubMed
-
- Fiorenza F, Abudu A, Grimer RJ, et al. Risk factors for survival and local control in chondrosarcoma of bone. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002;84:93–99. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
