Zinc finger protein 667 expression is upregulated by cerebral ischemic preconditioning and protects cells from oxidative stress
- PMID: 24648981
- PMCID: PMC3917004
- DOI: 10.3892/br.2013.124
Zinc finger protein 667 expression is upregulated by cerebral ischemic preconditioning and protects cells from oxidative stress
Abstract
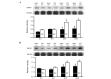
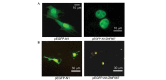
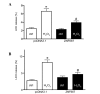
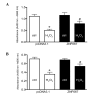
Brain ischemic injury is associated with clinical emergencies such as acute ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke, head trauma, prolonged severe hypotension and cardiac arrest. Ischemic preconditioning (IPC) is the most powerful endogenous mechanism against ischemic injury. However, the majority of IPC treatments are invasive and thus impractical in the clinical setting. Identifying the endogenous neuroprotective mechanism induced by IPC is important for developing new strategies to reduce stroke severity. Zinc finger protein 667 (ZNF667) is a novel zinc finger protein that is upregulated by myocardial IPC. However, its functional role in neuronal ischemia has not been elucidated. In this study, the changes of ZNF667 expression on cerebral IPC and its potential neuroprotective function were investigated. The cerebral ischemia model was established by ameliorated four-vessel occlusion in rats. The northern blot results demonstrated that ZNF667 expression was increased in the hippocampus and cortex at 12 and 24 h after cerebral ischemic pretreatment. To investigate the neuroprotective function of ZNF667, enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP)-ZNF667 fusion protein was expressed in C2C12 and brain astrocytoma cells and its subcellular localization was detected by confocal microscopy. EGFP-ZNF667 fusion proteins were localized in the nucleus of C2C12 and brain astrocytoma cells, indicating that ZNF667 may act as a transcription factor in neural cells. To mimic oxidative stress associated with ischemia/reperfusion injury, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) was used to treat cells. Cell viability was measured by the lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and WST-1 assays. A decrease in viability was detected in C2C12 and astrocytoma cells following H2O2 treatment, whereas ZNF667 gene overexpression significantly improved cell viability following H2O2 treatment. These results suggested that ZNF667 plays a neuroprotective role by acting as a transcription factor in cerebral IPC.
Keywords: cell protection; cerebral ischemic preconditioning; gene expression; oxidative stress; zinc finger protein 667.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ZNF667/Mipu1 is a novel anti-apoptotic factor that directly regulates the expression of the rat Bax gene in H9c2 cells.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 14;9(11):e111653. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111653. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25397408 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac Ischemic Preconditioning Promotes MG53 Secretion Through H2O2-Activated Protein Kinase C-δ Signaling.Circulation. 2020 Sep 15;142(11):1077-1091. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.044998. Epub 2020 Jul 17. Circulation. 2020. PMID: 32677469
-
ZNF667 attenuates leukocyte-endothelial adhesion via downregulation of P-selectin in skin flap following remote limb ischemic preconditioning.Cell Biol Int. 2021 Jul;45(7):1477-1486. doi: 10.1002/cbin.11586. Epub 2021 Mar 18. Cell Biol Int. 2021. PMID: 33710682
-
Genetics and genomics of ischemic tolerance: focus on cardiac and cerebral ischemic preconditioning.Pharmacogenomics. 2012 Nov;13(15):1741-57. doi: 10.2217/pgs.12.157. Pharmacogenomics. 2012. PMID: 23171338 Review.
-
Cross-talk of intracellular calcium stores in the response to neuronal ischemia and ischemic tolerance.Gen Physiol Biophys. 2009;28 Spec No Focus:F104-14. Gen Physiol Biophys. 2009. PMID: 20093720 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuroprotective and neuro-rehabilitative effects of acute purinergic receptor P2X4 (P2X4R) blockade after ischemic stroke.Exp Neurol. 2020 Jul;329:113308. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113308. Epub 2020 Apr 11. Exp Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32289314 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc Finger Proteins in Neuro-Related Diseases Progression.Front Neurosci. 2021 Nov 18;15:760567. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.760567. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34867169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aberrant methylation and downregulation of ZNF667-AS1 and ZNF667 promote the malignant progression of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma.J Biomed Sci. 2019 Jan 26;26(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s12929-019-0506-0. J Biomed Sci. 2019. PMID: 30684967 Free PMC article.
-
Modelling the Human Blood-Brain Barrier in Huntington Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 15;23(14):7813. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147813. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35887162 Free PMC article.
-
ZNF667 facilitates angiogenesis after myocardial ischemia through transcriptional regulation of VASH1 and Wnt signaling pathway.Int J Mol Med. 2022 Oct;50(4):129. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2022.5185. Epub 2022 Aug 31. Int J Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 36043524 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Donnan GA, Fisher M, Macleod M, Davis SM. Stroke. Lancet. 2008;371:1612–1623. - PubMed
-
- Zemke D, Smith JL, Reeves MJ, Majid A. Ischemia and ischemic tolerance in the brain: an overview. Neurotoxicology. 2004;25:895–904. - PubMed
-
- Stenzel-Poore MP, Stevens SL, Simon RP. Genomics of preconditioning. Stroke. 2004;35:2683–2686. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
