Effects of apoptosis-related proteins caspase-3, Bax and Bcl-2 on cerebral ischemia rats
- PMID: 24649043
- PMCID: PMC3917099
- DOI: 10.3892/br.2013.153
Effects of apoptosis-related proteins caspase-3, Bax and Bcl-2 on cerebral ischemia rats
Abstract
Neuron apoptosis is known to mediate a change of ethology following cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Additionally, Bcl-2, Bax and caspase-3 proteins may exert a significant effect on neuron injury. The aim of this study was to investigate the role, mechanism of action and clinical significance of these proteins in neuron apoptosis and functional impairment following cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Sixty male healthy adult Wistar rats were randomly assigned into control (n=6), sham operation (n=6) and experimental (n=48) groups. The model of rat cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury was set up according to the method of Zea-Longa. Eight subsets of 6 rats-subset were designed according to time points (at 3, 6, 12, 24 and 48 h and at 3, 7 and 14 days). Nerve functional injury was evaluated and graded using nerve function score, balance, coordination function detection and measurement of forelimb placing. The neurons expressing caspase-3, Bax and Bcl-2 in the cortical area, CA3, CA1, stratum lucidum (Slu) and molecular layer of the dentate gyrus (MoDG) of the hippocampus were detected using immunohistochemistry or the TUNEL method. The expression of caspase-3, Bax and Bcl-2 genes was detected by the reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). The results indicated that, compared to the sham operation group, the score of nerve function and balance beam walking were distinctly higher (P<0.01) and the percentage of rat foreleg touching the angle or margin of the table was significantly lower in the experimental rat group (P<0.01) at 3 h following reperfusion. The expression of TUNEL-positive neurons was high in the cortical area and the CA3 region of the hippocampus (P<0.01), caspase-3 was at peak value in the cortical area and the CA1 region of the hippocampus (P<0.01), Bax was increased in the cortical area and the Slu of the hippocampus (P<0.01) and Bcl-2 was low in the cortical area and the MoDG of the hippocampus (P<0.01) in the experimental group at 48 h following reperfusion. In conclusion, cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury may cause neurological impairment and lead to a change of ethology, and neuron apoptosis may be associated with the activation of caspase-3 and Bax and the downregulation of Bcl-2.
Keywords: Bax; Bcl-2; caspase-3; cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury; neurological impairment; neuron apoptosis.
Figures

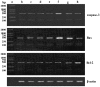
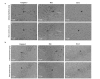
References
-
- Candelario-Jalil E. Injury and repair mechanisms in ischemic stroke: considerations for the development of novel neurotherapeutics. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2009;10:644–654. - PubMed
-
- Li Q, Zhang R, Guo YL, Mei YW. Effect of neuregulin on apoptosis and expressions of STAT3 and GFAP in rats following cerebral ischemic reperfusion. J Mol Neurosci. 2009;37:67–73. - PubMed
-
- Li Q, Zhang R, Ge YL, Mei YW, Guo YL. Effects of neuregulin on expression of MMP-9 and NSE in brain of ischemia/reperfusion rat. J Mol Neurosci. 2009;38:207–215. - PubMed
-
- Longa EZ, Weistein PR, Calson S, et al. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 1989;20:84–89. - PubMed
-
- Bederson JB, Pitts LH, Tsuji M, et al. Rat middle cerebral artery occlusion: evaluation of the model and development of a neurologic examination. Stroke. 1986;17:472–476. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
