The S protein of hepatitis B virus promotes collagen type I expression in hepatic stellate cells by virtue of hepatocytes
- PMID: 24649077
- PMCID: PMC3917019
- DOI: 10.3892/br.2013.201
The S protein of hepatitis B virus promotes collagen type I expression in hepatic stellate cells by virtue of hepatocytes
Abstract
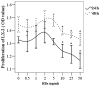
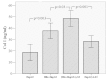
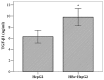
This study was conducted in order to investigate whether hepatitis B surface S protein (HBs) was able to directly or indirectly promote the proliferation and expression of collagen type I (Col I) and α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) in hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). The LX-2 human cell line and the HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line were employed as HSCs and as hepatocytes, respectively. Recombinant HBs was added to the LX-2 cells for 48 h and the cell proliferation was assessed by the MTT assay. Col I and α-SMA were measured in the supernatant by ELISA, following treatment of the LX-2 and/or HepG2 cells with recombinant HBs. Transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) was also determined by ELISA in the HepG2 cell supernatants. The data demonstrated that high concentrations of recombinant HBs (10-50 ng/ml) inhibited the proliferation of LX-2 cells, whereas low concentrations (0.5-5 ng/ml) did not affect LX-2 cell proliferation. After treating LX-2 cells alone with recombinant HBs for 48 h, there was no significant increase in the Col I and α-SMA levels. However, Col I was increased ~1.7-fold in co-cultured (LX-2 and HepG2) cell supernatants following treatment with HBs for 24 h (HBs vs. control group: 48.51±3.51 vs. 28.23±2.55 ng/ml, respectively). Furthermore, TGF-β1 was significantly increased in the HepG2 cell supernatants following treatment with recombinant HBs. Therefore, we concluded that HBs directly affected the proliferation of HSCs, but promoted the Col I expression in HSCs possibly by virtue of hepatocytes secreting TGF-β1. This may provide a novel explanation of the fibrogenetic mechanism induced by hepatitis B virus-related proteins.
Keywords: LX-2 cell line; S protein; fibrosis; hepatic stellate cells; hepatitis B virus.
Figures
References
-
- Ocama P, Opio CK, Lee WM. Hepatitis B virus infection: current status. Am J Med. 2005;118:1413. - PubMed
-
- Lavanchy D. Hepatitis B virus epidemiology, disease burden, treatment, and current and emerging prevention and control measures. J Viral Hepat. 2004;11:97–107. - PubMed
-
- Kao JH, Chen DS. Global control of hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet Infect Dis. 2002;2:395–403. - PubMed
-
- Lee WM. Hepatitis B virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:1733–1745. - PubMed
-
- Ganem D, Prince AM. Hepatitis B virus infection - natural history and clinical consequences. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1118–1129. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
