Antitumoral effect of PLK-1-inhibitor BI2536 in combination with cisplatin and docetaxel in squamous cell carcinoma cell lines of the head and neck
- PMID: 24649162
- PMCID: PMC3956268
- DOI: 10.3892/mco.2012.45
Antitumoral effect of PLK-1-inhibitor BI2536 in combination with cisplatin and docetaxel in squamous cell carcinoma cell lines of the head and neck
Abstract
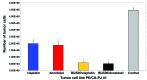
Inhibition of the polo-like-kinase-1 (PLK-1) has been shown to be effective in several haematological and solid tumor models. In this systemic in vitro study, the antitumor effect of BI2536, a small molecule inhibitor of PLK-1, in combination with cisplatin and docetaxel was examined in nine squamous cell carcinoma cell lines, most of which had a head and neck origin (SCCHN). Dose escalation studies were conducted with nine SCCHN cell lines using BI2536, cisplatin and docetaxel in cell line-specific concentrations. Growth inhibitory and proapoptotic effects were measured quantitatively using cytohistology and a Human Apoptose Array kit. BI2536 in combination with cisplatin and docetaxel showed a markedly higher antiproliferative and apoptotic activity in the SCCHN cell lines investigated (P≤0.008), compared with single agent cisplatin or docetaxel alone. The findings of this study showed that the addition of PLK-1-inhibitor BI2536 to conventional chemotherapeutic drugs led to a statistically higher antiproliferative and apoptotic effect in SCCHN cell lines compared with cisplatin or docetaxel alone. Inaugurating BI2536 in the clinical setting might enhance the antitumoral activity of conventional drugs, possibly leading to less toxic side effects of cancer therapy.
Keywords: BI2536; apoptosis; cisplatin; docetaxel; growth inhibition; squamous cell head and neck carcinoma cell lines.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Small molecules in combination with conventional chemotherapeutic drugs: Light at the end of the tunnel?Oncol Lett. 2012 Nov;4(5):1043-1046. doi: 10.3892/ol.2012.883. Epub 2012 Aug 28. Oncol Lett. 2012. PMID: 23162648 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the Polo-like-kinase-1-inhibitor BI2536 in squamous cell carcinoma cell lines of the head and neck.Oncol Lett. 2012 Jul;4(1):175-177. doi: 10.3892/ol.2012.700. Epub 2012 Apr 30. Oncol Lett. 2012. PMID: 22807983 Free PMC article.
-
Fighting cancer from different signalling pathways: Effects of the proteasome inhibitor Bortezomib in combination with the polo-like-kinase-1-inhibitor BI2536 in SCCHN.Oncol Lett. 2012 Dec;4(6):1305-1308. doi: 10.3892/ol.2012.927. Epub 2012 Sep 20. Oncol Lett. 2012. PMID: 23226805 Free PMC article.
-
Docetaxel in squamous cell cancer of the head and neck.Anticancer Drugs. 2001 Feb;12 Suppl 1:S21-4. Anticancer Drugs. 2001. PMID: 11340900 Review.
-
The Evolving and Future Role of Taxanes in Squamous Cell Carcinomas of the Head and Neck: A Review.JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016 Sep 1;142(9):898-905. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2016.1238. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016. PMID: 27389786 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting the Mitotic Catastrophe Signaling Pathway in Cancer.Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:146282. doi: 10.1155/2015/146282. Epub 2015 Sep 27. Mediators Inflamm. 2015. PMID: 26491220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Programmed cell death, redox imbalance, and cancer therapeutics.Apoptosis. 2021 Aug;26(7-8):385-414. doi: 10.1007/s10495-021-01682-0. Epub 2021 Jul 8. Apoptosis. 2021. PMID: 34236569 Review.
-
Mutations of the LIM protein AJUBA mediate sensitivity of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma to treatment with cell-cycle inhibitors.Cancer Lett. 2017 Apr 28;392:71-82. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.01.024. Epub 2017 Jan 23. Cancer Lett. 2017. PMID: 28126323 Free PMC article.
-
The Polo-like kinase 1 inhibitor onvansertib represents a relevant treatment for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma resistant to cisplatin and radiotherapy.Theranostics. 2021 Sep 21;11(19):9571-9586. doi: 10.7150/thno.61711. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 34646387 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mehanna H, Paleri V, West CM, Nutting C. Head and neck cancer - Part 1: Epidemiology, presentation, and prevention. BMJ. 2010;341:c4684. - PubMed
-
- Wagenblast J, Hambek M, Baghi M, Gstöttner W, Strebhardt K, Ackermann H, Knecht R. Antiproliferative activity of bortezomib alone and in combination with cisplatin or docetaxel in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2008;134:323–330. - PubMed
-
- Strebhardt K. Multifaceted polo-like kinases: drug targets and antitargets for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010;9:643–660. - PubMed
-
- Barr FA, Sillje HH, Nigg EA. Polo-like kinases and the orchestration of cell division. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5:429–440. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
