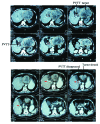
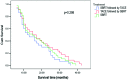
Stereotactic body radiotherapy combined with transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis
- PMID: 24649306
- PMCID: PMC3916201
- DOI: 10.3892/mco.2013.196
Stereotactic body radiotherapy combined with transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the clinical efficacy, toxicity and adverse effects of stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) combined with transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with portal vein tumor thrombosis (PVTT). A total of 101 patients diagnosed with primary HCC with PVTT were enrolled in this study and were randomly divided into three groups as follows: group A, 34 patients treated with γ-SBRT followed by TACE; group B, 37 patients treated with TACE followed by γ-SBRT; and group C, 30 patients treated with γ-SBRT alone. The effective response rate for the entire patient sample was 87.1% (88/101) following a 3-month treatment. The differences in the response rate, survival rate, α-fetoprotein level restoration rate and rate of improvement of abdominal distention and discomfort between groups A and B were not statistically significant (P>0.05). However, the rates of groups A and B were higher compared to those of group C (P<0.05). The exacerbation rate of liver function in group A was lower compared to that in group B (P<0.05), although it exhibited no statistically significant difference from that in group C (P>0.05). No severe radiation-related complications were reported during the follow-up period. The combination of γ-SBRT and TACE was shown to be a relatively effective local treatment for primary HCC patients with PVTT. Compared to γ-SBRT followed by TACE and γ-SBRT alone, TACE followed by γ-SBRT may exert a negative effect on liver function. These results suggested that the combination of TACE and γ-SBRT may be considered a relatively effective, safe and feasible treatment method for primary HCC patients with PVTT, although TACE followed by γ-SBRT may negatively affect liver function.
Keywords: portal vein tumor thrombosis; primary hepatocellular carcinoma; stereotactic body radiotherapy; transcatheter arterial chemoembolization; γ-knife.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Stereotactic body radiotherapy based treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma with extensive portal vein tumor thrombosis.Radiat Oncol. 2018 Sep 25;13(1):188. doi: 10.1186/s13014-018-1136-5. Radiat Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30253783 Free PMC article.
-
Stereotactic body radiotherapy plus transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma patients with portal vein tumour thrombus: A meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2022 May 20;17(5):e0268779. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0268779. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35594278 Free PMC article.
-
[Comparison of therapeutics effects of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization combined with iodine-125 seed implantation and sorafenib for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2018 Apr 20;26(4):298-304. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2018.04.013. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29996343 Chinese.
-
Is hepatocellular carcinoma complicated with portal vein tumor thrombosis potentially curable by radiotherapy in the form of stereotactic body radiation therapy?Int J Radiat Biol. 2022;98(10):1495-1509. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2022.2055800. Epub 2022 Apr 4. Int J Radiat Biol. 2022. PMID: 35311612 Review.
-
The Current Role of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) in Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC).Cancers (Basel). 2022 Sep 8;14(18):4383. doi: 10.3390/cancers14184383. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36139545 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombus in China (2021 Edition).Liver Cancer. 2022 Mar 17;11(4):315-328. doi: 10.1159/000523997. eCollection 2022 Jul. Liver Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35978596 Free PMC article.
-
Stereotactic body radiotherapy as the initial treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma with extensive inferior vena cava and atrium tumor thrombus.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Jul 4;12:5299-5303. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S208560. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 31308700 Free PMC article.
-
Cyberknife treatment for advanced or terminal stage hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Dec 14;21(46):13101-12. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i46.13101. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26673627 Free PMC article.
-
Management strategies for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis.Ewha Med J. 2025 Jan;48(1):e4. doi: 10.12771/emj.2025.e4. Epub 2025 Jan 31. Ewha Med J. 2025. PMID: 40704194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiotherapy for liver tumors.Hepat Oncol. 2015 Apr;2(2):133-146. doi: 10.2217/hep.15.7. Epub 2015 Apr 20. Hepat Oncol. 2015. PMID: 30190993 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Farazi PA, DePinho RA. Hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis: from genes to environment. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:674–687. - PubMed
-
- Yang HI, Lu SN, Liaw YF, et al. Hepatitis B e antigen and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:168–174. - PubMed
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM. Updated treatment approach to hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol. 2005;40:225–235. - PubMed
-
- Cabibbo G, Enea M, Attanasio M, Bruix J, Craxi A, Camma C. A meta-analysis of survival rates of untreated patients in randomized clinical trials of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2010;51:1274–1283. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous