Isolation of Intestinal Parasites of Public Health Importance from Cockroaches (Blattella germanica) in Jimma Town, Southwestern Ethiopia
- PMID: 24649356
- PMCID: PMC3932213
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/186240
Isolation of Intestinal Parasites of Public Health Importance from Cockroaches (Blattella germanica) in Jimma Town, Southwestern Ethiopia
Abstract
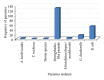
Cockroaches are claimed to be mechanical transmitters of disease causing microorganisms such as intestinal parasites, bacteria, fungi, and viruses. This study assessed the potential of the German cockroach Blattella germanica in the mechanical transmission of intestinal parasites of public health importance. A total of 2010 cockroaches were collected from 404 households in Jimma Town, southwestern Ethiopia. All the collected cockroaches were identified to species as B. germanica. The contents of their gut and external body parts were examined for the presence of intestinal parasites. Overall, 152 (75.6%) of the 210 batches were found to harbor at least one species of human intestinal parasite. Ascaris lumbricoides, Trichuris trichiura, Taenia spp, Strongyloides-like parasite, Entamoeba histolytica/dispar/moshkovski, Giardia duodenalis and Balantidium coli were detected from gut contents. Moreover, parasites were also isolated from the external surface in 22 (10.95%) of the batches. There was significant difference in parasite carriage rate of the cockroaches among the study sites (P = 0.013). In conclusion, B. germanica was found to harbor intestinal parasites of public health importance. Hence, awareness on the potential role of cockroaches in the mechanical transmission of human intestinal parasites needs to be created. Moreover, further identification of the Strongyloides-like worm is required using molecular diagnostics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Domiciliary Cockroaches as Carriers of Human Intestinal Parasites in Lagos Metropolis, Southwest Nigeria: Implications for Public Health.J Arthropod Borne Dis. 2018 Jun 13;12(2):141-151. eCollection 2018 Jun. J Arthropod Borne Dis. 2018. PMID: 30123808 Free PMC article.
-
Cockroaches as carriers of human intestinal parasites in two localities in Ethiopia.Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2008 Nov;102(11):1143-7. doi: 10.1016/j.trstmh.2008.05.009. Epub 2008 Jun 25. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2008. PMID: 18579170
-
Prevalence of Parasitic Contamination of Cockroaches Collected from Fresh Markets in Chachoengsao Province, Thailand.Kobe J Med Sci. 2020 Feb 10;65(4):E118-E123. Kobe J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32201426 Free PMC article.
-
Contamination of cockroaches (Insecta: Blattaria) to medically fungi: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Mycol Med. 2017 Dec;27(4):427-448. doi: 10.1016/j.mycmed.2017.04.012. Epub 2017 May 11. J Mycol Med. 2017. PMID: 28506564
-
Contamination of Cockroaches (Insecta: Blattaria) by Medically Important Bacteriae: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.J Med Entomol. 2019 Oct 28;56(6):1534-1554. doi: 10.1093/jme/tjz095. J Med Entomol. 2019. PMID: 31219601
Cited by
-
Rapid evolutionary responses to insecticide resistance management interventions by the German cockroach (Blattella germanica L.).Sci Rep. 2019 Jun 5;9(1):8292. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-44296-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31165746 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Underpinnings of Cuticular Hydrocarbon Biosynthesis in the German Cockroach, Blattella germanica (L.): Progress and Perspectives.J Chem Ecol. 2024 Dec;50(12):955-968. doi: 10.1007/s10886-024-01509-7. Epub 2024 May 10. J Chem Ecol. 2024. PMID: 38727793 Review.
-
Pathogens of Medical Importance Identified in Hospital-Collected Cockroaches: A Systematic Review.Microorganisms. 2025 Feb 4;13(2):337. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13020337. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40005704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Systematic Review of Zoonotic Enteric Parasites Carried by Flies, Cockroaches, and Dung Beetles.Pathogens. 2022 Jan 13;11(1):90. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11010090. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 35056038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intestinal Parasites Associated with American Cockroach (Periplaneta americana) in Akure, Ondo State, Nigeria.J Parasit Dis. 2024 Mar;48(1):67-73. doi: 10.1007/s12639-024-01645-7. Epub 2024 Jan 25. J Parasit Dis. 2024. PMID: 38440767 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kumie A, Genete K, Worku H, Kebede E, Ayele H Mulugeta F. The sanitary conditions of public food and drink establishments in the district town of Zeway, Southern Ethiopia. Ethiopian Journal of Health Development. 2002;16(1):95–104.
-
- Gullan PJ, Cranston PS. The Insects: An Outline of Entomology. Davis, Calif, USA: Blackwell; 2005.
-
- Salehzadeh A, Tavacol P, Mahjub H. Bacterial, fungal and parasitic contamination of cockroaches in public hospitals of Hamadan, Iran. Journal of Vector Borne Diseases. 2007;44(2):105–110. - PubMed
-
- Baumholtz MA, Parish LC, Witkowski JA, Nutting WB. The medical importance of cockroaches. International Journal of Dermatology. 1997;36(2):90–96. - PubMed
-
- Al-bayati NY, Al-Ubaidi AS, Al-Ubaidi IK. Risks associated with cockroach Periplaneta americana as a transmitter of pathogen agents. Diyala Journal of Medicine. 2011;1(1):91–97.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous