Enhancement of recombinant myricetin on the radiosensitivity of lung cancer A549 and H1299 cells
- PMID: 24650056
- PMCID: PMC3994494
- DOI: 10.1186/1746-1596-9-68
Enhancement of recombinant myricetin on the radiosensitivity of lung cancer A549 and H1299 cells
Abstract
Objective: Myricetin, a common dietary flavonoid is widely distributed in fruits and vegetables, and is used as a health food supplement based on its immune function, anti-oxidation, anti-tumor, and anti-inflammatory properties. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of myricetin on combination with radiotherapy enhance radiosensitivity of lung cancer A549 and H1299 cells.
Methods: A549 cells and H1299 cells were exposed to X-ray with or without myricetin treatment. Colony formation assays, CCK-8 assay, flow cytometry and Caspase-3 level detection were used to evaluate the radiosensitization activity of myricetin on cell proliferation and apoptosis in vitro. Nude mouse tumor xenograft model was built to assessed radiosensitization effect of myricetin in vivo.
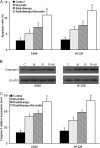
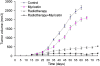
Results: Compared with the exposed group without myricetin treatment, the groups treated with myricetin showed significantly suppressed cell surviving fraction and proliferation, increased the cell apoptosis and increased Caspase-3 protein expression after X-ray exposure in vitro. And in vivo assay, growth speed of tumor xenografts was significantly decreased in irradiated mice treated with myricetin.
Conclusions: The study demonstrated both in vitro and in vivo evidence that combination of myricetin with radiotherapy can enhance tumor radiosensitivity of pulmonary carcinoma A549 and H1299 cells, and myricetin could be a potential radiosensitizer for lung cancer therapy.
Virtual slides: The virtual slide(s) for this article can be found here: http://www.diagnosticpathology.diagnomx.eu/vs/5791518001210633.
Figures

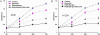
Similar articles
-
Radiosensitization effect of quinoline-indole-schiff base derivative 10E on non-small cell lung cancer cells in vitro and in tumor xenografts.Invest New Drugs. 2024 Aug;42(4):405-417. doi: 10.1007/s10637-024-01451-1. Epub 2024 Jun 17. Invest New Drugs. 2024. PMID: 38880855
-
Berberine inhibits the expression of hypoxia induction factor-1alpha and increases the radiosensitivity of prostate cancer.Diagn Pathol. 2014 May 27;9:98. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-9-98. Diagn Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24886405 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and in vivo radiosensitization with AZD6244 (ARRY-142886), an inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 kinase.Clin Cancer Res. 2009 May 1;15(9):3050-7. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2954. Epub 2009 Apr 14. Clin Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19366835 Free PMC article.
-
Myricetin: targeting signaling networks in cancer and its implication in chemotherapy.Cancer Cell Int. 2022 Jul 28;22(1):239. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02663-2. Cancer Cell Int. 2022. PMID: 35902860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myricetin: A comprehensive review on its biological potentials.Food Sci Nutr. 2021 Aug 11;9(10):5854-5868. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.2513. eCollection 2021 Oct. Food Sci Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34646551 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anticancer effects of myricetin derivatives in non-small cell lung cancer in vitro and in vivo.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2022 Feb;10(1):e00905. doi: 10.1002/prp2.905. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2022. PMID: 34964301 Free PMC article.
-
Myricetin induces apoptosis by inhibiting P21 activated kinase 1 (PAK1) signaling cascade in hepatocellular carcinoma.Mol Cell Biochem. 2015 Sep;407(1-2):223-37. doi: 10.1007/s11010-015-2471-6. Epub 2015 Jun 24. Mol Cell Biochem. 2015. PMID: 26104578
-
Myricetin bioactive effects: moving from preclinical evidence to potential clinical applications.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020 Aug 1;20(1):241. doi: 10.1186/s12906-020-03033-z. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020. PMID: 32738903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
South Asian Medicinal Compounds as Modulators of Resistance to Chemotherapy and Radiotherapy.Cancers (Basel). 2016 Mar 5;8(3):32. doi: 10.3390/cancers8030032. Cancers (Basel). 2016. PMID: 26959063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiation-induced ferroptosis via liposomal delivery of 7-Dehydrocholesterol.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Mar 26;23(1):249. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03303-3. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40133959 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nygren P, Glimelius B. The Swedish Council on Technology Assessment in Health Care (SBU) report on Cancer Chemotherapy–Project objectives, the working process, key definitions and general aspects on cancer trial methodology and interpretation. Acta Oncol. 2001;40:155–165. doi: 10.1080/02841860151116187. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

