Linac-based stereotactic radiotherapy and radiosurgery in patients with meningioma
- PMID: 24650090
- PMCID: PMC4028108
- DOI: 10.1186/1748-717X-9-78
Linac-based stereotactic radiotherapy and radiosurgery in patients with meningioma
Abstract
Background: It was our purpose to analyze long-term clinical outcome and to identify prognostic factors after Linac-based fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy (Linac-based FSRT) and stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) in patients with intracranial meningiomas.
Materials and methods: Between 10/1995 and 03/2009, 297 patients with a median age of 59 years were treated with FSRT for intracranial meningioma. 50 patients had a Grade I meningioma, 20 patients had a Grade II meningioma, 12 patients suffered from a Grade III tumor, and in 215 cases no histology was obtained (Grade 0). Of the 297 patients, 144 underwent FSRT as their primary treatment and 158 underwent postoperative FSRT. 179 patients received normofractionated radiotherapy (nFSRT), 92 patients received hypofractionated FSRT (hFSRT) and 26 patients underwent SRS. Patients with nFSRT received a mean total dose of 57.31 ± 5.82 Gy, patients with hFSRT received a mean total dose of 37.6 ± 4.4 Gy and patients who underwent SRS received a mean total dose of 17.31 ± 2.58 Gy.
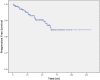
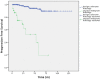
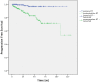
Results: Median follow-up was 35 months. Overall progression free survival (PFS) was 92.3% at 3 years, 87% at 5 years and 84.1% at 10 years. Patients with adjuvant radiotherapy showed significantly better PFS-rates than patients who had been treated with primary radiotherapy. There was no significant difference between PFS-rates of nFSRT, hFSRT and SRS patients. PFS-rates were independent of tumor size. Patients who had received nFSRT showed less acute toxicity than those who had received hFSRT. In the Grade 0/I group the rate of radiologic focal reactions was significantly lower than in the atypical/malignant histology group.
Conclusion: This large study showed that FSRT is an effective and safe treatment modality with high PFS-rates for intracranial meningioma. We identified "pathological grading" and and "prior surgery" as significant prognostic factors.
Figures



References
-
- Milker-Zabel S, Zabel-du Bois A, Huber P, Schlegel W, Debus J. Fractionated stereotactic radiation therapy in the management of benign cavernous sinus meningiomas : long-term experience and review of the literature. Strahlentherapie und Onkologie: Organ der Deutschen Rontgengesellschaft. 2006;182:635–640. doi: 10.1007/s00066-006-1548-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Thilmann C, Schulz-Ertner D, Unterberg A, Wannenmacher M, Debus J. Stereotaktische strahlenbehandlung schädelbasisnaher meningeome und schwannome. Dtsch Arztebl. 2004;Heft 15:1022–1026.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

