Maize IgE binding proteins: each plant a different profile?
- PMID: 24650160
- PMCID: PMC3999935
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-5956-12-17
Maize IgE binding proteins: each plant a different profile?
Abstract
Background: Allergies are nearly always triggered by protein molecules and the majority of individuals with documented immunologic reactions to foods exhibit IgE hypersensitivity reactions. In this study we aimed to understand if natural differences, at proteomic level, between maize populations, may induce different IgE binding proteins profiles among maize-allergic individuals. We also intended to deepen our knowledge on maize IgE binding proteins.
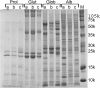
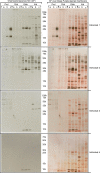
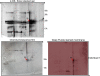
Results: In order to accomplish this goal we have used proteomic tools (SDS-PAGE and 2-D gel electrophoresis followed by western blot) and tested plasma IgE reactivity from four maize-allergic individuals against four different protein fractions (albumins, globulins, glutelins and prolamins) of three different maize cultivars. We have observed that maize cultivars have different proteomes that result in different IgE binding proteins profiles when tested against plasma from maize-allergic individuals. We could identify 19 different maize IgE binding proteins, 11 of which were unknown to date. Moreover, we found that most (89.5%) of the 19 identified potential maize allergens could be related to plant stress.
Conclusions: These results lead us to conclude that, within each species, plant allergenic potential varies with genotype. Moreover, considering the stress-related IgE binding proteins identified, we hypothesise that the environment, particularly stress conditions, may alter IgE binding protein profiles of plant components.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Lipid-transfer protein is the major maize allergen maintaining IgE-binding activity after cooking at 100 degrees C, as demonstrated in anaphylactic patients and patients with positive double-blind, placebo-controlled food challenge results.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003 Oct;112(4):775-83. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(03)01942-0. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003. PMID: 14564361 Clinical Trial.
-
Cultivar-specific IgE-epitopes in date (Phoenix dactylifera L.) fruit allergy. Correlation of skin test reactivity and ige-binding properties in selecting date cultivars for allergen standardization.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2000 Oct;123(2):137-44. doi: 10.1159/000024432. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2000. PMID: 11060485
-
The maize major allergen, which is responsible for food-induced allergic reactions, is a lipid transfer protein.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000 Oct;106(4):744-51. doi: 10.1067/mai.2000.108712. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000. PMID: 11031346
-
Two-dimensional electrophoresis and IgE-mediated food allergy.Electrophoresis. 2010 Jul;31(13):2126-36. doi: 10.1002/elps.201000101. Electrophoresis. 2010. PMID: 20593388 Review.
-
Parasite allergens.Mol Immunol. 2018 Aug;100:113-119. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2018.03.014. Epub 2018 Mar 24. Mol Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29588070 Review.
Cited by
-
High IgE sensitization to maize and rice pollen in the highlands of Madagascar.Pan Afr Med J. 2014 Nov 15;19:284. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2014.19.284.4654. eCollection 2014. Pan Afr Med J. 2014. PMID: 25870739 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Novel Short Ragweed Pollen Allergens Using Combined Transcriptomic and Immunoproteomic Approaches.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 28;10(8):e0136258. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136258. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26317427 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Ligustrum pollen: New insights into allergic disease.World Allergy Organ J. 2020 Feb 5;13(2):100104. doi: 10.1016/j.waojou.2020.100104. eCollection 2020 Feb. World Allergy Organ J. 2020. PMID: 32055279 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into ragweed pollen allergens.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2015 Nov;15(11):63. doi: 10.1007/s11882-015-0565-6. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2015. PMID: 26383916 Review.
-
Known Allergen Structures Predict Schistosoma mansoni IgE-Binding Antigens in Human Infection.Front Immunol. 2015 Feb 3;6:26. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00026. eCollection 2015. Front Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25691884 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brown W, Zuber M, Darrah L, Glover D. Origin, Adaptation, and Types of Corn. National Corn Handbook; The corn crop NCH-10. 1985. pp. 1–6. http://corn.agronomy.wisc.edu/Management/pdfs/NCH10.pdf.
-
- Pastorello EA, Farioli L, Pravettoni V, Scibilia J, Conti A, Fortunato D, Borgonovo L, Bonomi S, Primavesi L, Ballmer-Weber B. Maize food allergy: lipid-transfer proteins, endochitinases, and alpha-zein precursor are relevant maize allergens in double-blind placebo-controlled maize-challenge-positive patients. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2009;395:93–102. doi: 10.1007/s00216-009-2945-z. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kottapalli KR, Payton P, Rakwal R, Agrawal GK, Shibato J, Burow M, Puppala N. Proteomics analysis of mature seed of four peanut cultivars using two-dimensional gel electrophoresis reveals distinct differential expression of storage, anti-nutritional, and allergenic proteins. Plant Sci. 2008;175:321–329. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2008.05.005. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

