Influence of calcium in extracellular DNA mediated bacterial aggregation and biofilm formation
- PMID: 24651318
- PMCID: PMC3961253
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091935
Influence of calcium in extracellular DNA mediated bacterial aggregation and biofilm formation
Abstract
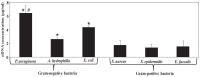
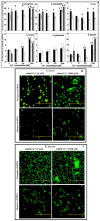
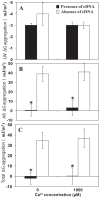
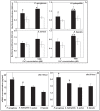
Calcium (Ca(2+)) has an important structural role in guaranteeing the integrity of the outer lipopolysaccharide layer and cell walls of bacterial cells. Extracellular DNA (eDNA) being part of the slimy matrix produced by bacteria promotes biofilm formation through enhanced structural integrity of the matrix. Here, the concurrent role of Ca(2+) and eDNA in mediating bacterial aggregation and biofilm formation was studied for the first time using a variety of bacterial strains and the thermodynamics of DNA to Ca(2+) binding. It was found that the eDNA concentrations under both planktonic and biofilm growth conditions were different among bacterial strains. Whilst Ca(2+) had no influence on eDNA release, presence of eDNA by itself favours bacterial aggregation via attractive acid-base interactions in addition, its binding with Ca(2+) at biologically relevant concentrations was shown further increase in bacterial aggregation via cationic bridging. Negative Gibbs free energy (ΔG) values in iTC data confirmed that the interaction between DNA and Ca(2+) is thermodynamically favourable and that the binding process is spontaneous and exothermic owing to its highly negative enthalpy. Removal of eDNA through DNase I treatment revealed that Ca(2+) alone did not enhance cell aggregation and biofilm formation. This discovery signifies the importance of eDNA and concludes that existence of eDNA on bacterial cell surfaces is a key facilitator in binding of Ca(2+) to eDNA thereby mediating bacterial aggregation and biofilm formation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa Requires the DNA-Specific Endonuclease EndA To Degrade Extracellular Genomic DNA To Disperse from the Biofilm.J Bacteriol. 2019 Aug 22;201(18):e00059-19. doi: 10.1128/JB.00059-19. Print 2019 Sep 15. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 30988033 Free PMC article.
-
Pyocyanin facilitates extracellular DNA binding to Pseudomonas aeruginosa influencing cell surface properties and aggregation.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58299. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058299. Epub 2013 Mar 11. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23505483 Free PMC article.
-
Release mechanisms and molecular interactions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa extracellular DNA.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Aug;104(15):6549-6564. doi: 10.1007/s00253-020-10687-9. Epub 2020 Jun 4. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32500267 Review.
-
Extracellular DNA is essential for maintaining Bordetella biofilm integrity on abiotic surfaces and in the upper respiratory tract of mice.PLoS One. 2011 Feb 11;6(2):e16861. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016861. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21347299 Free PMC article.
-
The role of extracellular DNA in the establishment, maintenance and perpetuation of bacterial biofilms.Crit Rev Microbiol. 2015;41(3):341-52. doi: 10.3109/1040841X.2013.841639. Epub 2013 Dec 4. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 24303798 Review.
Cited by
-
Flow-assembled chitosan membranes in microfluidics: recent advances and applications.J Mater Chem B. 2021 Apr 21;9(15):3258-3283. doi: 10.1039/d1tb00045d. Epub 2021 Mar 16. J Mater Chem B. 2021. PMID: 33725061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Lifecycle: Involvement of Mechanical Constraints and Timeline of Matrix Production.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Jul 24;13(8):688. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13080688. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Study of Nanosized Silicate-Substituted Hydroxyapatites Co-Doped with Sr2+ and Zn2+ Ions Related to Their Influence on Biological Activities.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022 Dec 9;44(12):6229-6246. doi: 10.3390/cimb44120425. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 36547086 Free PMC article.
-
Corrected and republished from: "Vibrio fischeri Possesses Xds and Dns Nucleases That Differentially Influence Phosphate Scavenging, Aggregation, Competence, and Symbiotic Colonization of Squid".Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024 Jun 18;90(6):e0032824. doi: 10.1128/aem.00328-24. Epub 2024 May 7. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38712952 Free PMC article.
-
The Antibacterial and Anti-biofilm Activity of Metal Complexes Incorporating 3,6,9-Trioxaundecanedioate and 1,10-Phenanthroline Ligands in Clinical Isolates of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa from Irish Cystic Fibrosis Patients.Antibiotics (Basel). 2020 Oct 5;9(10):674. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9100674. Antibiotics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33027987 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stoodley HL, Costerton WJ, Stoodley P (2004) Bacterial biofilms: from the natural environment to infectious diseases. Nat Rev Microbiol 2: 95–108. - PubMed
-
- Beech IB, Sunner J (2004) Biocorrosion: towards understanding interactions between biofilms and metals. Curr Opin Biotechnol 15: 181–186. - PubMed
-
- Lee M, Low A, Zemb O, Koenig J, Michaelsen A, et al. (2012) Complete chloroform dechlorination by organochlorine respiration and fermentation. Environ Microbiol 14: 883–894. - PubMed
-
- Venkataraman A, Rosenbaum M, Arends jan BA, Halitschke R, Angenent LT (2010) Quorum sensing regulates electric current generations of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA14 in bioelectrochemical systems. Electrochem Communications 12: 459–462.
-
- Shoji T, Ochi S, Masaaki OM (2008) Characterization of bacterial biofilm communities in tertiary treatment processes for wastewater reclamation and reuse. Water. Sci. Technol. 58: 1023–1030. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

