MicroRNA-23a/b and microRNA-27a/b suppress Apaf-1 protein and alleviate hypoxia-induced neuronal apoptosis
- PMID: 24651435
- PMCID: PMC3973202
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2014.92
MicroRNA-23a/b and microRNA-27a/b suppress Apaf-1 protein and alleviate hypoxia-induced neuronal apoptosis
Abstract
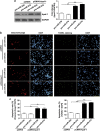
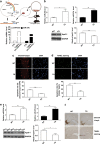
Expression of apoptotic protease activating factor-1 (Apaf-1) gradually decreases during brain development, and this decrease is likely responsible for the decreased sensitivity of brain tissue to apoptosis. However, the mechanism by which Apaf-1 expression is decreased remains elusive. In the present study, we found that four microRNAs (miR-23a/b and miR-27a/b) of miR-23a-27a-24 and miR-23b-27b-24 clusters play key roles in modulating the expression of Apaf-1. First, we found that miR-23a/b and miR-27a/b suppressed the expression of Apaf-1 in vitro. Interestingly, the expression of the miR-23-27-24 clusters in the mouse cortex gradually increased in a manner that was inversely correlated with the pattern of Apaf-1 expression. Second, hypoxic injuries during fetal distress caused reduced expression of the miR-23b and miR-27b that was inversely correlated with an elevation of Apaf-1 expression during neuronal apoptosis. Third, we made neuronal-specific transgenic mice and found that overexpressing the miR-23b and miR-27b in mouse neurons inhibited the neuronal apoptosis induced by intrauterine hypoxia. In conclusion, our results demonstrate, in central neural system, that miR-23a/b and miR-27a/b are endogenous inhibitory factors of Apaf-1 expression and regulate the sensitivity of neurons to apoptosis. Our findings may also have implications for the potential target role of microRNAs in the treatment of neuronal apoptosis-related diseases.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-23a antisense enhances 5-fluorouracil chemosensitivity through APAF-1/caspase-9 apoptotic pathway in colorectal cancer cells.J Cell Biochem. 2014 Apr;115(4):772-84. doi: 10.1002/jcb.24721. J Cell Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24249161
-
Downregulation of miR-23a and miR-27a following experimental traumatic brain injury induces neuronal cell death through activation of proapoptotic Bcl-2 proteins.J Neurosci. 2014 Jul 23;34(30):10055-71. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1260-14.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25057207 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of miR-27a sensitizes colorectal cancer stem cells to TRAIL by promoting the formation of Apaf-1-caspase-9 complex.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 11;8(28):45213-45223. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16779. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28423356 Free PMC article.
-
Interactive functions of microRNAs in the miR-23a-27a-24-2 cluster and the potential for targeted therapy in cancer.J Cell Physiol. 2020 Jan;235(1):6-16. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28958. Epub 2019 Jun 13. J Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31192453 Review.
-
Distinct microRNA expression pattern in breast cancer cells following anti-neoplastic treatment: A systematic review and functional analysis of microRNA target genes.Malays J Pathol. 2022 Dec;44(3):367-385. Malays J Pathol. 2022. PMID: 36591707
Cited by
-
microRNAs associated with the pathogenesis and their role in regulating various signaling pathways during Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Oct 27;12:1009901. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1009901. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36389170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Implications of Epigenetic Dysregulation in Perinatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Damage.Front Neurol. 2020 Jun 9;11:483. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00483. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32582011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Upregulation of microRNA-23a regulates proliferation and apoptosis by targeting APAF-1 in laryngeal carcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2015 Jul;10(1):410-416. doi: 10.3892/ol.2015.3238. Epub 2015 May 20. Oncol Lett. 2015. PMID: 26171041 Free PMC article.
-
Response of plasma microRNAs to nusinersen treatment in patients with SMA.Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2022 Jul;9(7):1011-1026. doi: 10.1002/acn3.51579. Epub 2022 May 18. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35584175 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs: protective regulators for neuron growth and development.Neural Regen Res. 2023 Apr;18(4):734-745. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.353481. Neural Regen Res. 2023. PMID: 36204829 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nijhawan D, Honarpour N, Wang X. Apoptosis in neural development and disease. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2000;23:73–87. - PubMed
-
- Kuida K, Zheng TS, Na S, Kuan C, Yang D, Karasuyama H, et al. Decreased apoptosis in the brain and premature lethality in CPP32-deficient mice. Nature. 1996;384:368–372. - PubMed
-
- Hakem R, Hakem A, Duncan GS, Henderson JT, Woo M, Soengas MS, et al. Differential requirement for caspase 9 in apoptotic pathways in vivo. Cell. 1998;94:339–352. - PubMed
-
- Yoshida H, Kong YY, Yoshida R, Elia AJ, Hakem A, Hakem R, et al. Apaf1 is required for mitochondrial pathways of apoptosis and brain development. Cell. 1998;94:739–750. - PubMed
-
- Thompson CB. Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science. 1995;267:1456–1462. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

