iNR-Drug: predicting the interaction of drugs with nuclear receptors in cellular networking
- PMID: 24651462
- PMCID: PMC3975431
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms15034915
iNR-Drug: predicting the interaction of drugs with nuclear receptors in cellular networking
Abstract
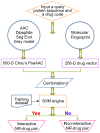
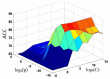
Nuclear receptors (NRs) are closely associated with various major diseases such as cancer, diabetes, inflammatory disease, and osteoporosis. Therefore, NRs have become a frequent target for drug development. During the process of developing drugs against these diseases by targeting NRs, we are often facing a problem: Given a NR and chemical compound, can we identify whether they are really in interaction with each other in a cell? To address this problem, a predictor called "iNR-Drug" was developed. In the predictor, the drug compound concerned was formulated by a 256-D (dimensional) vector derived from its molecular fingerprint, and the NR by a 500-D vector formed by incorporating its sequential evolution information and physicochemical features into the general form of pseudo amino acid composition, and the prediction engine was operated by the SVM (support vector machine) algorithm. Compared with the existing prediction methods in this area, iNR-Drug not only can yield a higher success rate, but is also featured by a user-friendly web-server established at http://www.jci-bioinfo.cn/iNR-Drug/, which is particularly useful for most experimental scientists to obtain their desired data in a timely manner. It is anticipated that the iNR-Drug server may become a useful high throughput tool for both basic research and drug development, and that the current approach may be easily extended to study the interactions of drug with other targets as well.
Figures

Similar articles
-
iNR-PhysChem: a sequence-based predictor for identifying nuclear receptors and their subfamilies via physical-chemical property matrix.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e30869. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030869. Epub 2012 Feb 21. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22363503 Free PMC article.
-
iGPCR-drug: a web server for predicting interaction between GPCRs and drugs in cellular networking.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 27;8(8):e72234. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072234. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24015221 Free PMC article.
-
NR-2L: a two-level predictor for identifying nuclear receptor subfamilies based on sequence-derived features.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23505. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023505. Epub 2011 Aug 15. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21858146 Free PMC article.
-
Predict drug-protein interaction in cellular networking.Curr Top Med Chem. 2013;13(14):1707-12. doi: 10.2174/15680266113139990121. Curr Top Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23889048 Review.
-
Recent progresses in identifying nuclear receptors and their families.Curr Top Med Chem. 2013;13(10):1192-200. doi: 10.2174/15680266113139990006. Curr Top Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23647541 Review.
Cited by
-
A high performance prediction of HPV genotypes by Chaos game representation and singular value decomposition.BMC Bioinformatics. 2015 Mar 5;16:71. doi: 10.1186/s12859-015-0493-4. BMC Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 25880169 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Sub-Nuclear Localization Based on Effective Fusion Representations and Dimension Reduction Algorithm LDA.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Dec 19;16(12):30343-61. doi: 10.3390/ijms161226237. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26703574 Free PMC article.
-
iRNA-PseColl: Identifying the Occurrence Sites of Different RNA Modifications by Incorporating Collective Effects of Nucleotides into PseKNC.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2017 Jun 16;7:155-163. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2017.03.006. Epub 2017 Mar 29. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2017. PMID: 28624191 Free PMC article.
-
3D QSAR studies, pharmacophore modeling and virtual screening on a series of steroidal aromatase inhibitors.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Nov 14;15(11):20927-47. doi: 10.3390/ijms151120927. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25405729 Free PMC article.
-
Protein subnuclear localization based on a new effective representation and intelligent kernel linear discriminant analysis by dichotomous greedy genetic algorithm.PLoS One. 2018 Apr 12;13(4):e0195636. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0195636. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29649330 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altucci L., Gronemeyer H. Nuclear receptors in cell life and death. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2001;12:460–468. - PubMed
-
- Bates M.K., Kerr R.M. Nuclear Receptors. Nova Science; Hauppauge, NY, USA: 2011.
-
- Bunce C.M., Campbell M.J. Nuclear Receptors: Current Concepts and Future Challenges. Springer; Dordrecht, The Netherlands; New York, NY, USA: 2010. p. xii.p. 457.
-
- Robinson-Rechavi M., Garcia H.E., Laudet V. The nuclear receptor superfamily. J. Cell Sci. 2003;116:585–586. - PubMed
-
- Kastner P. Non-steroid nuclear receptors: What are genetic studies telling us their role in renal life? Cell. 1995;83:859–869. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

