Visceral adiposity index (VAI) is predictive of an altered adipokine profile in patients with type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 24651545
- PMCID: PMC3961281
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091969
Visceral adiposity index (VAI) is predictive of an altered adipokine profile in patients with type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Aims: Although there is still no clear definition of "adipose tissue dysfunction" or ATD, the identification of a clinical marker of altered fat distribution and function may provide the needed tools for early identification of a condition of cardiometabolic risk. Our aim was to evaluate the correlations among various anthropometric indices [BMI, Waist Circumference (WC), Hip Circumference (HC), Waist/Hip ratio (WHR), Body Adiposity Index (BAI) and Visceral adiposity Index (VAI)] and several adipocytokines [Visfatin, Resistin, Leptin, Soluble leptin receptors (sOB-R), Adiponectin, Ghrelin, Adipsin, PAI-1, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) TNF-α, hs-CRP, IL-6, IL-18] in patients with type 2 diabetes (DM2).
Materials and methods: Ninety-one DM2 patients (age: 65.25 ± 6.38 years; 42 men and 49 women) in stable treatment for the last six months with metformin in monotherapy (1.5-2 g/day) were cross-sectionally studied. Clinical, anthropometric, and metabolic parameters were evaluated. Serum adipocytokine levels were assayed with Luminex based kits.
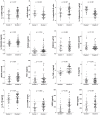
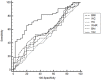
Results: At the Pearson's correlation, among all the indices investigated, VAI showed a significant correlation with almost all adipocytokines analyzed [Visfatin, Resistin and hsCRP (all p<0.001); Adiponectin, sOb-R, IL-6, IL-18, HGF (all p<0.010); Ghrelin and VEGF (both p<0.05)]. Through a two-step cluster analysis, 55 patients were identified with the most altered adipocytokine profile (patients with ATD). At a ROC analysis, VAI showed the highest C-statistic [0.767 (95% CI 0.66-0.84)] of all the indices.
Conclusions: Our study suggests that the VAI, among the most common indexes of adiposity assessment, shows the best correlation with the best known adipocytokines and cardiometabolic risk serum markers. Although to date we are still far from clearly identifying an ATD, the VAI would be an easy tool for clearly mirroring a condition of cardiometabolic risk, in the absence of an overt metabolic syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- De Fronzo RA, Ferrannini E (1991) Insulin resistance. A multifaceted syndrome responsible for NIDDM, obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Care 14: 173–194. - PubMed
-
- Després JP (2012) Body fat distribution and risk of cardiovascular disease: an update. Circulation 126: 1301–1301. - PubMed
-
- Abbasi F, Brown BW Jr, Lamendola C, Mc Laughlin T, Reaven GM (2002) Relationship between obesity, insulin resistance, and coronary heart disease risk. J Am Coll Cardiol 40: 937–943. - PubMed
-
- Bays H, Abate N, Chandalia M (2005) Adiposopathy: sick fat causes high blood sugar, high blood pressure and dyslipidemia. Future Cardiol 1: 39–59. - PubMed
-
- Ruderman N, Chisholm D, Pi-Sunyer X, Schneider S (1998) The metabolically obese, normal-weight individual revisited. Diabetes 47: 699–713. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

