Macrophage inflammatory markers are associated with subclinical carotid artery disease in women with human immunodeficiency virus or hepatitis C virus infection
- PMID: 24651679
- PMCID: PMC4067091
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.303153
Macrophage inflammatory markers are associated with subclinical carotid artery disease in women with human immunodeficiency virus or hepatitis C virus infection
Abstract
Objective: Infection with hepatitis C virus (HCV) or human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) may be associated with atherosclerosis and vascular disease. Macrophages are a major component of atherosclerotic plaque, and classically activated (M1) macrophages contribute to plaque instability. Our goal was to identify plasma biomarkers that reflect macrophage inflammation and are associated with subclinical atherosclerosis.
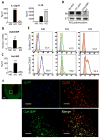
Approach and results: We tested whether M1 macrophages produce galectin-3-binding protein in vitro. Then, we measured galectin-3-binding protein and the soluble macrophage biomarkers soluble cluster of differentiation (CD) 163 and soluble CD14 in 264 participants in the Women's Interagency HIV Study. Women were positive for HIV, HCV, both, or neither (66 in each group, matched for age, race/ethnicity, and smoking status). Carotid artery disease was assessed by ultrasound measurement of right distal common carotid artery intima-media thickness, distensibility, and presence of atherosclerotic lesions (intima-media thickness >1.5 mm). Plasma galectin-3-binding protein was higher in HCV+ than HCV- women (P<0.01) but did not differ by HIV status. The 3 inflammatory macrophage markers were significantly correlated with each other and negatively correlated with CD4+ counts in HIV-infected women. We defined a macrophage score as 1, 2, or 3 biomarkers elevated above the median. In models adjusted for traditional risk factors, higher macrophage scores were significantly associated with increased atherosclerotic lesions and lower carotid distensibility. Receiver-operator curve analysis of lesions revealed that the markers added predictive value beyond traditional risk factors and C-reactive protein.
Conclusions: The macrophage inflammatory markers galectin-3-binding protein, soluble CD163, and soluble CD14 are significantly associated with carotid artery disease in the setting of HIV and HCV infection.
Keywords: acquired immunodeficiency syndrome; atherosclerosis; immune system; risk factors; women.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Libby P, Ridker PM. Inflammation and atherosclerosis: role of C-reactive protein in risk assessment. Am J Med. 2004;116(Suppl 6A):9S–16S. - PubMed
-
- Stoger JL, Gijbels MJ, van der Velden S, Manca M, van der Loos CM, Biessen EA, Daemen MJ, Lutgens E, de Winther MP. Distribution of macrophage polarization markers in human atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 2012;225:461–468. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01-HL-095140/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI103397/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI031834/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL095140/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-034993/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034989/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-103401/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000454/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-103397/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI103401/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000004/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI103408/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-103390/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-034994/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-103408/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035004/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH083579/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-083760/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK026743/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL083760/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-035004/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034994/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL115232/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-034989/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-042590/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-HD-032632/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI103390/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034993/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-031834/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD032632/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI042590/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

