Identification of a small molecular insulin receptor agonist with potent antidiabetes activity
- PMID: 24651808
- PMCID: PMC3964510
- DOI: 10.2337/db13-0334
Identification of a small molecular insulin receptor agonist with potent antidiabetes activity
Abstract
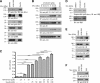
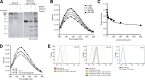
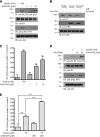
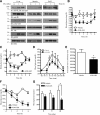
Insulin replacement therapy is a widely adopted treatment for all patients with type 1 diabetes and some with type 2 diabetes. However, injection of insulin has suffered from problems such as tissue irritation, abscesses, discomfort, and inconvenience. The use of orally bioactive insulin mimetics thus represents an ideal treatment alternative. Here we show that a chaetochromin derivative (4548-G05) acts as a new nonpeptidyl insulin mimetic. 4548-G05 selectively activates an insulin receptor (IR) but not insulin-like growth factor receptor-I or other receptor tyrosine kinases. Through binding to the extracellular domain of the IR, 4548-G05 induces activation of the receptor and initiates the downstream Akt and extracellular signal-related kinase pathways to trigger glucose uptake in C2C12 myotubes. Moreover, it displays a potent blood glucose-lowering effect when administrated orally in normal, type 1 diabetic, and type 2 diabetic mice models. Therefore, 4548-G05 may represent a novel pharmacological agent for antidiabetes drug development.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification of a molecular activator for insulin receptor with potent anti-diabetic effects.J Biol Chem. 2011 Oct 28;286(43):37379-88. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.247387. Epub 2011 Sep 9. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21908618 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of a small molecule insulin receptor activator.Recent Prog Horm Res. 2001;56:107-26. doi: 10.1210/rp.56.1.107. Recent Prog Horm Res. 2001. PMID: 11237209
-
A Small Insulinomimetic Molecule Also Improves Insulin Sensitivity in Diabetic Mice.PLoS One. 2017 Jan 10;12(1):e0169809. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169809. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28072841 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of diabetes with vanadium salts: general overview and amelioration of nutritionally induced diabetes in the Psammomys obesus gerbil.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2001 Jan-Feb;17(1):55-66. doi: 10.1002/1520-7560(2000)9999:9999<::aid-dmrr165>3.0.co;2-j. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2001. PMID: 11241892 Review.
-
Diabetes, Obesity, COVID-19, Insulin, and Other Antidiabetes Drugs.Diabetes Care. 2021 Sep;44(9):1929-1933. doi: 10.2337/dci21-0003. Epub 2021 Jul 8. Diabetes Care. 2021. PMID: 34244331 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of the Anti-Diabetic Activity of Some Common Herbs and Spices: Providing New Insights with Inverse Virtual Screening.Molecules. 2019 Nov 7;24(22):4030. doi: 10.3390/molecules24224030. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31703341 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A high-throughput chemical-genetics screen in murine adipocytes identifies insulin-regulatory pathways.J Biol Chem. 2019 Mar 15;294(11):4103-4118. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.006986. Epub 2018 Dec 27. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30591588 Free PMC article.
-
Higher-Resolution Structure of the Human Insulin Receptor Ectodomain: Multi-Modal Inclusion of the Insert Domain.Structure. 2016 Mar 1;24(3):469-76. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2015.12.014. Epub 2016 Feb 12. Structure. 2016. PMID: 26853939 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of the interaction between ribosomal protein L10a and insulin receptor on carbohydrate metabolism.Heliyon. 2020 Dec 15;6(12):e05714. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05714. eCollection 2020 Dec. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 33364490 Free PMC article.
-
Non-peptidyl small molecule, adenosine, 5'-Se-methyl-5'-seleno-, 2',3'-diacetate, activates insulin receptor and attenuates hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetic Leprdb/db mice.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020 Apr;77(8):1623-1643. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03249-4. Epub 2019 Aug 5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 31378829 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saltiel AR, Kahn CR. Insulin signalling and the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Nature 2001;414:799–806 - PubMed
-
- Desvergne B, Michalik L, Wahli W. Transcriptional regulation of metabolism. Physiol Rev 2006;86:465–514 - PubMed
-
- Campbell RK. Type 2 diabetes: where we are today: an overview of disease burden, current treatments, and treatment strategies. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003) 2009;49(Suppl. 1):S3–S9 - PubMed
-
- Richardson T, Kerr D. Skin-related complications of insulin therapy: epidemiology and emerging management strategies. Am J Clin Dermatol 2003;4:661–667 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

