Identification of a small molecular insulin receptor agonist with potent antidiabetes activity
- PMID: 24651808
- PMCID: PMC3964510
- DOI: 10.2337/db13-0334
Identification of a small molecular insulin receptor agonist with potent antidiabetes activity
Abstract
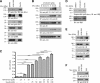
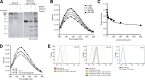
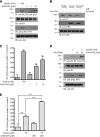
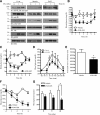
Insulin replacement therapy is a widely adopted treatment for all patients with type 1 diabetes and some with type 2 diabetes. However, injection of insulin has suffered from problems such as tissue irritation, abscesses, discomfort, and inconvenience. The use of orally bioactive insulin mimetics thus represents an ideal treatment alternative. Here we show that a chaetochromin derivative (4548-G05) acts as a new nonpeptidyl insulin mimetic. 4548-G05 selectively activates an insulin receptor (IR) but not insulin-like growth factor receptor-I or other receptor tyrosine kinases. Through binding to the extracellular domain of the IR, 4548-G05 induces activation of the receptor and initiates the downstream Akt and extracellular signal-related kinase pathways to trigger glucose uptake in C2C12 myotubes. Moreover, it displays a potent blood glucose-lowering effect when administrated orally in normal, type 1 diabetic, and type 2 diabetic mice models. Therefore, 4548-G05 may represent a novel pharmacological agent for antidiabetes drug development.
Figures


References
-
- Saltiel AR, Kahn CR. Insulin signalling and the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Nature 2001;414:799–806 - PubMed
-
- Desvergne B, Michalik L, Wahli W. Transcriptional regulation of metabolism. Physiol Rev 2006;86:465–514 - PubMed
-
- Campbell RK. Type 2 diabetes: where we are today: an overview of disease burden, current treatments, and treatment strategies. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003) 2009;49(Suppl. 1):S3–S9 - PubMed
-
- Richardson T, Kerr D. Skin-related complications of insulin therapy: epidemiology and emerging management strategies. Am J Clin Dermatol 2003;4:661–667 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

