Cross-talk between sirtuin and mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) signaling in the regulation of S6 kinase 1 (S6K1) phosphorylation
- PMID: 24652283
- PMCID: PMC4036325
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.520734
Cross-talk between sirtuin and mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) signaling in the regulation of S6 kinase 1 (S6K1) phosphorylation
Abstract
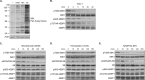
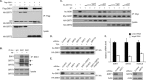
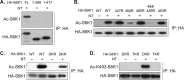
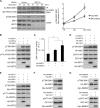
p70 ribosomal S6 kinase (S6K1), a major substrate of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) kinase, regulates diverse cellular processes including protein synthesis, cell growth, and survival. Although it is well known that the activity of S6K1 is tightly coupled to its phosphorylation status, the regulation of S6K1 activity by other post-translational modifications such as acetylation has not been well understood. Here we show that the acetylation of the C-terminal region (CTR) of S6K1 blocks mTORC1-dependent Thr-389 phosphorylation, an essential phosphorylation site for S6K1 activity. The acetylation of the CTR of S6K1 is inhibited by the class III histone deacetylases, SIRT1 and SIRT2. An S6K1 mutant lacking acetylation sites in its CTR shows enhanced Thr-389 phosphorylation and kinase activity, whereas the acetylation-mimetic S6K1 mutant exhibits decreased Thr-389 phosphorylation and kinase activity. Interestingly, relative to the acetylation-mimetic S6K1 mutant, the acetylation-defective mutant displays higher affinity toward Raptor, an essential scaffolding component of mTORC1 that recruits mTORC1 substrates. These observations indicate that sirtuin-mediated regulation of S6K1 acetylation is an additional important regulatory modification that impinges on the mechanisms underlying mTORC1-dependent S6K1 activation.
Keywords: Acetylation; Phosphorylation; Rapamycin; S6 Kinase; Sirt1; Sirtuins; mTOR; mTOR Complex (mTORC).
Figures

References
-
- Magnuson B., Ekim B., Fingar D. C. (2012) Regulation and function of ribosomal protein S6 kinase (S6K) within mTOR signalling networks. Biochem. J. 441, 1–21 - PubMed
-
- Saitoh M., ten Dijke P., Miyazono K., Ichijo H. (1998) Cloning and characterization of p70S6Kβ defines a novel family of p70 S6 kinases. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 253, 470–476 - PubMed
-
- Lee-Fruman K. K., Kuo C. J., Lippincott J., Terada N., Blenis J. (1999) Characterization of S6K2, a novel kinase homologous to S6K1. Oncogene 18, 5108–5114 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

