The N-terminal domain modulates α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptor desensitization
- PMID: 24652293
- PMCID: PMC4036331
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.526301
The N-terminal domain modulates α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptor desensitization
Abstract
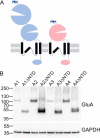
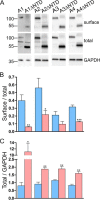
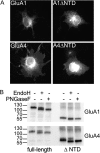
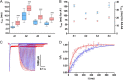
AMPA receptors are tetrameric glutamate-gated ion channels that mediate fast synaptic neurotransmission in mammalian brain. Their subunits contain a two-lobed N-terminal domain (NTD) that comprises over 40% of the mature polypeptide. The NTD is not obligatory for the assembly of tetrameric receptors, and its functional role is still unclear. By analyzing full-length and NTD-deleted GluA1-4 AMPA receptors expressed in HEK 293 cells, we found that the removal of the NTD leads to a significant reduction in receptor transport to the plasma membrane, a higher steady state-to-peak current ratio of glutamate responses, and strongly increased sensitivity to glutamate toxicity in cell culture. Further analyses showed that NTD-deleted receptors display both a slower onset of desensitization and a faster recovery from desensitization of agonist responses. Our results indicate that the NTD promotes the biosynthetic maturation of AMPA receptors and, for membrane-expressed channels, enhances the stability of the desensitized state. Moreover, these findings suggest that interactions of the NTD with extracellular/synaptic ligands may be able to fine-tune AMPA receptor-mediated responses, in analogy with the allosteric regulatory role demonstrated for the NTD of NMDA receptors.
Keywords: Allosteric Regulation; Ion Channels; Ionotropic Glutamate Receptors (AMPA, NMDA); Protein Domains; Receptor Desensitization; Receptor Structure-Function.
Figures


References
-
- Clayton A., Siebold C., Gilbert R. J., Sutton G. C., Harlos K., McIlhinney R. A., Jones E. Y., Aricescu A. R. (2009) Crystal structure of the GluR2 amino-terminal domain provides insights into the architecture and assembly of ionotropic glutamate receptors. J. Mol. Biol. 392, 1125–1132 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

