State medicaid coverage, ESRD incidence, and access to care
- PMID: 24652791
- PMCID: PMC4033371
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2013060658
State medicaid coverage, ESRD incidence, and access to care
Abstract
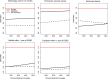
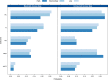
The proportion of low-income nonelderly adults covered by Medicaid varies widely by state. We sought to determine whether broader state Medicaid coverage, defined as the proportion of each state's low-income nonelderly adult population covered by Medicaid, associates with lower state-level incidence of ESRD and greater access to care. The main outcomes were incidence of ESRD and five indicators of access to care. We identified 408,535 adults aged 20-64 years, who developed ESRD between January 1, 2001, and December 31, 2008. Medicaid coverage among low-income nonelderly adults ranged from 12.2% to 66.0% (median 32.5%). For each additional 10% of the low-income nonelderly population covered by Medicaid, there was a 1.8% (95% confidence interval, 1.0% to 2.6%) decrease in ESRD incidence. Among nonelderly adults with ESRD, gaps in access to care between those with private insurance and those with Medicaid were narrower in states with broader coverage. For a 50-year-old white woman, the access gap to the kidney transplant waiting list between Medicaid and private insurance decreased by 7.7 percentage points in high (>45%) versus low (<25%) Medicaid coverage states. Similarly, the access gap to transplantation decreased by 4.0 percentage points and the access gap to peritoneal dialysis decreased by 3.8 percentage points in high Medicaid coverage states. In conclusion, states with broader Medicaid coverage had a lower incidence of ESRD and smaller insurance-related access gaps.
Copyright © 2014 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
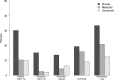
Comment in
-
Health insurance, access to care, and ESRD: an intricate web.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014 Jun;25(6):1135-6. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2014010122. Epub 2014 Mar 20. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24652805 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Cantor JC, Long SH, Marquis S: Challenges of state health reform: Variations in ten states. Health Aff (Millwood) 17: 191–200, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Coughlin TA, Long SK, Shen YC: Assessing access to care under Medicaid: Evidence for the nation and thirteen states. Health Aff (Millwood) 24: 1073–1083, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Weissman JS, Zaslavsky AM, Wolf RE, Ayanian JZ: State Medicaid coverage and access to care for low-income adults. J Health Care Poor Underserved 19: 307–319, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Coughlin TA, Long SK: Adult health care access and use under Medicaid: Does it vary by state? J Health Care Poor Underserved 14: 208–228, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Hoffman C, Schwartz K: Eroding access among nonelderly U.S. adults with chronic conditions: Ten years of change. Health Aff (Millwood) 27: w340–w348, 2008 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

