Clinical analysis of chinese patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with leflunomide and methotrexate combined with different dosages of glucocorticoid
- PMID: 24653514
- PMCID: PMC3954009
- DOI: 10.1016/j.curtheres.2012.06.001
Clinical analysis of chinese patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with leflunomide and methotrexate combined with different dosages of glucocorticoid
Abstract
Objective: To analyze the safety of combined leflunomide (LEF), methotrexate (MTX), and glucocorticoid (GC) therapy, we investigated the adverse effects of such combination therapy in patients with early active rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods: Two hundred sixty-six patients with RA who were receiving LEF and MTX therapy were randomly assigned to 3 groups, as follows: group 1 received no GC, group 2 received 7.5 mg prednisone, and group 3 received 15 mg prednisone. Adverse effects were analyzed using the χ(2) test at week 4 or the Fisher exact test at week 12.
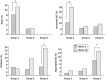
Results: Patients in group 1 had a higher incidence of skin rash, oral ulcers, leukopenia, and liver damage than did those in groups 2 and 3 (all, P ≤ 0.05). However, the rates of osteoporosis, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and hypertension in group 3 were statistically higher than in groups 1 and 2 (P ≤ 0.05).
Conclusion: In the treatment of RA, the incidence of skin rash, liver dysfunction, and oral ulcers may be decreased with combination therapy using LEF, MTX, and 7.5 mg prednisone, and blood pressure, blood glucose concentration, and bone density are not increased. Most important, 7.5 mg prednisone was synergistic with LEF and MTX, and such combination therapy could be a useful option as initial treatment of early active RA.
Keywords: adverse reactions; glucocorticoid; leflunomide; methotrexate; rheumatoid arthritis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of maintenance therapy with methotrexate compared with leflunomide for patients with RA having achieved disease control with both these drugs: results of a predefined sub-analysis of CareRA, a pragmatic RCT.Clin Rheumatol. 2020 Sep;39(9):2593-2601. doi: 10.1007/s10067-020-05008-4. Epub 2020 Mar 12. Clin Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32166429 Clinical Trial.
-
Two-year, blinded, randomized, controlled trial of treatment of active rheumatoid arthritis with leflunomide compared with methotrexate. Utilization of Leflunomide in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis Trial Investigator Group.Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Sep;44(9):1984-92. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200109)44:9<1984::AID-ART346>3.0.CO;2-B. Arthritis Rheum. 2001. PMID: 11592358 Clinical Trial.
-
Preliminary evaluation in rheumatoid arthritis activity in patients treated with TNF-alpha blocker plus methotrexate versus methotrexate or leflunomide alone.Rheumatol Int. 2007 May;27(7):641-7. doi: 10.1007/s00296-006-0272-7. Epub 2007 Jan 18. Rheumatol Int. 2007. PMID: 17235556 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical safety of total glucosides of paeony adjuvant therapy for rheumatoid arthritis treatment: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021 Mar 26;21(1):102. doi: 10.1186/s12906-021-03252-y. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021. PMID: 33771151 Free PMC article.
-
[Systematic reviews of effects of Tripterygium Glycosides Tablets on pro-inflammatory factors in rheumatoid arthritis].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020 Feb;45(4):764-774. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20191024.401. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32237476 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Neutropenia in the Elderly: A Rheumatology Perspective.Drugs Aging. 2016 Aug;33(8):585-601. doi: 10.1007/s40266-016-0383-0. Drugs Aging. 2016. PMID: 27402172 Review.
-
Use of corticoids and non-steroidal anti-inflammatories in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: Systematic review and network meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2021 Apr 7;16(4):e0248866. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248866. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33826610 Free PMC article.
-
Non-pharmacological and pharmacological interventions in patients with early arthritis: a systematic literature review informing the 2016 update of EULAR recommendations for the management of early arthritis.RMD Open. 2017 Jan 5;3(1):e000404. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2016-000404. eCollection 2017. RMD Open. 2017. PMID: 28151539 Free PMC article.
-
Can active components of licorice, glycyrrhizin and glycyrrhetinic acid, lick rheumatoid arthritis?Oncotarget. 2016 Jan 12;7(2):1193-202. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6200. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26498361 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sokka T. Work disability in early rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheum. 2003;21(Suppl 31):71–74. - PubMed
-
- Borchers A.T., Keen C.L., Cheema G.S., Gershwin M.E. The use of methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2004;34:465–483. - PubMed
-
- Harris E.D. Rationale for combination therapy of rheumatoid arthritis based on pathophysiology. J Rheumatol. 1996;23:2–4. - PubMed
-
- Weinblatt M.A., Kremer J.M., Coblyn J.S. Pharmacokinetics, safety, and efficacy of combination treatment with methotrexate and leflunomide in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1999;42:1322–1328. - PubMed
-
- American College of Rheumatology Subcommittee on Rheumatoid Arthritis Guidelines Guidelines for the management of rheumatoid arthritis: 2002 update. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;136:328–346. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

