Chinese herbal medicine Shenqi Detoxification Granule inhibits fibrosis in adenine induced chronic renal failure rats
- PMID: 24653577
- PMCID: PMC3957265
- DOI: 10.4314/ajtcam.v11i1.31
Chinese herbal medicine Shenqi Detoxification Granule inhibits fibrosis in adenine induced chronic renal failure rats
Abstract
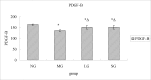
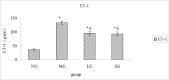
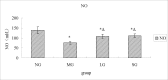
Background: Progressive fibrosis accompanies all chronic renal disease, connective tissue growth factor (CTGF,) and platelet-derived growth factor-B, (PDGF-B,) play important roles in extra-cellular matrix abnormal accumulation, while endothelin-1 (ET-1) nitric oxide (NO,) are related to endothelial dysfunction, which mediates the progression of renal fibrosis. Shenqi Detoxification Granule (SDG), a traditional Chinese herbal formula, has been used for treatment of chronic renal failure in clinic for many years.
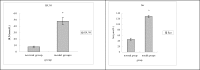
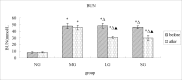
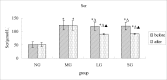
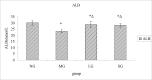
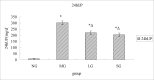
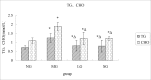
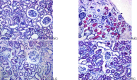
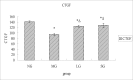
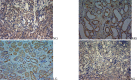
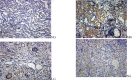
Materials and methods: In order to evaluate the efficacy, and explore the mechanism of SDG to inhibit the progression of renal fibrosis, study was carried out using the adenine-induced Wister rats as the CRF model, and losartan as postive control drug. Levels of serum creatinine [Scr], and blood urea nitrogen (BUN), albumin (ALB), 24hrs, urine protein (24hUP), triacylglycerol (TG), and cholesterol (CHO), together with ET-1, and NO were detected. Pathological changes of renal tissues were observed by HE, staining. In addition, CTGF and PDGF-B expression were analyzed by immuno-histo-chemistry.
Results: The results indicated that SDG can effectively reduce Scr, BUN, 24hUP, TG, and CHO levels, increase ALB levels, inhibit renal tissue damage in CRF rats, and the mechanism maybe reduce PDGF-B, CTGF expression and ET-1/NO.
Conclusion: Shenqi Detoxification Granule is a beneficial treatment for chronic renal failure.
Keywords: CTGF; Chronic Renal Failure; PDGF-B; Shenqi Detoxification Granule; fibrosis.
Figures
References
-
- Baylis C. Nitric oxide deficiency in chronic kidney disease. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008;294:F1–F9. - PubMed
-
- Brenner BM, Cooper ME, de Zeeuw D, Keane WF, Mitch WE, Parving HH, Remuzzi G, Snapinn SM, Zhang Z, Shahinfar S RENAAL Study Investigators, author. Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:861–869. - PubMed
-
- Brigstock DR. The connective tissue growth factor/cysteine-rich 61/ nephroblastoma overexpressed (CCN) family. Endocr Rev. 1999;20:189–206. - PubMed
-
- Chen XM, Li RH. The effect of Astragalus membranaceus on serum NO in patients with chronic glomerulonephritis at pre-renal failure phase. Journal of Chongqi Medical University. 2004;29:71–77. [Article in Chinese]
-
- Constans J, Conri C. Circulating markers of endothelial function in cardiovascular disease. Clin Chim Acta. 2006;368:33–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
